A novel regulatory mechanism of MAP kinases activation and nuclear translocation mediated by PKA and the PTP-SL tyrosine phosphatase
- PMID: 10601328
- PMCID: PMC2168101
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.147.6.1129
A novel regulatory mechanism of MAP kinases activation and nuclear translocation mediated by PKA and the PTP-SL tyrosine phosphatase
Abstract
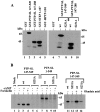
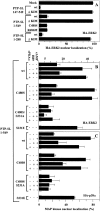
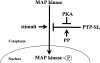
Protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP-SL retains mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases in the cytoplasm in an inactive form by association through a kinase interaction motif (KIM) and tyrosine dephosphorylation. The related tyrosine phosphatases PTP-SL and STEP were phosphorylated by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA). The PKA phosphorylation site on PTP-SL was identified as the Ser(231) residue, located within the KIM. Upon phosphorylation of Ser(231), PTP-SL binding and tyrosine dephosphorylation of the MAP kinases extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 and p38alpha were impaired. Furthermore, treatment of COS-7 cells with PKA activators, or overexpression of the Calpha catalytic subunit of PKA, inhibited the cytoplasmic retention of ERK2 and p38alpha by wild-type PTP-SL, but not by a PTP-SL S231A mutant. These findings support the existence of a novel mechanism by which PKA may regulate the activation and translocation to the nucleus of MAP kinases.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson N.G., Maller J.L., Tonks N.K., Sturgill T.W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990;343:651–653. - PubMed
-
- Brunet A., Pouysségur J. Identification of MAP kinase domains by redirecting stress signals into growth factor responses. Science. 1996;272:1652–1655. - PubMed
-
- Burgering B.M.T., Bos J.L. Regulation of Ras-mediated signallingmore than one way to skin a cat. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1995;20:18–22. - PubMed
-
- Chajry N., Martin P.-M., Cochet C., Berthois Y. Regulation of p42 mitogen-activated-protein kinase activity by protein phosphatase 2A under conditions of growth inhibition by epidermal growth factor in A431 cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996;235:97–102. - PubMed
-
- Cobb M.H., Goldsmith E.J. How MAP kinases are regulated. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:14843–14846. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

