Blood platelets are assembled principally at the ends of proplatelet processes produced by differentiated megakaryocytes
- PMID: 10601342
- PMCID: PMC2168104
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.147.6.1299
Blood platelets are assembled principally at the ends of proplatelet processes produced by differentiated megakaryocytes
Abstract
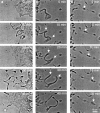
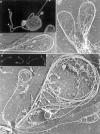
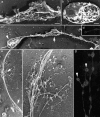
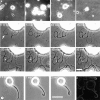
Megakaryocytes release mature platelets in a complex process. Platelets are known to be released from intermediate structures, designated proplatelets, which are long, tubelike extensions of the megakaryocyte cytoplasm. We have resolved the ultrastructure of the megakaryocyte cytoskeleton at specific stages of proplatelet morphogenesis and correlated these structures with cytoplasmic remodeling events defined by video microscopy. Platelet production begins with the extension of large pseudopodia that use unique cortical bundles of microtubules to elongate and form thin proplatelet processes with bulbous ends; these contain a peripheral bundle of microtubules that loops upon itself and forms a teardrop-shaped structure. Contrary to prior observations and assumptions, time-lapse microscopy reveals proplatelet processes to be extremely dynamic structures that interconvert reversibly between spread and tubular forms. Microtubule coils similar to those observed in blood platelets are detected only at the ends of proplatelets and not within the platelet-sized beads found along the length of proplatelet extensions. Growth and extension of proplatelet processes is associated with repeated bending and bifurcation, which results in considerable amplification of free ends. These aspects are inhibited by cytochalasin B and, therefore, are dependent on actin. We propose that mature platelets are assembled de novo and released only at the ends of proplatelets, and that the complex bending and branching observed during proplatelet morphogenesis represents an elegant mechanism to increase the numbers of proplatelet ends.
Figures




References
-
- An E., Ogata K., Kuriya S., Nomura T. Interleukin-6 and erythropoietin act as direct potentiators and inducers of in vitro cytoplasmic process formation on purified mouse megakaryocytes. Exp. Hematol. 1994;22:149–156. - PubMed
-
- Andrews R.K., Fox J.B. Interaction of purified actin-binding protein with glycoprotein Ib-IX complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:7144–7147. - PubMed
-
- Becker R.P., DeBruyn P.P. The transmural passage of blood cells into myeloid sinusoids and the entry of platelets into the sinusoidal circulationa scanning electron microscopic investigation. Am. J. Anat. 1976;145:1046–1052. - PubMed
-
- Behnke O. An electron microscope study of megakaryocytes of rat bone marrow. I. The development of the demarcation membrane system and the platelet surface coat. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1968;24:412–428. - PubMed
-
- Behnke O. An electron microscope study of the rat megakaryocyte. II. Some aspects of platelet release and microtubules. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1969;26:111–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

