Expression of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in pregnant human myometrium
- PMID: 10601500
- PMCID: PMC2269695
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.00705.x
Expression of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in pregnant human myometrium
Abstract
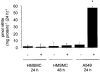
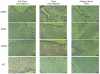
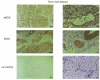
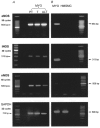
1. Endogenous nitric oxide has been proposed to play a role in the control of myometrial contractility in pregnancy. In this study, the expression, localisation and regulation of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) isoforms have been examined in human pregnant myometrium and cultured human myometrial smooth muscle cells, by immunoblotting, immunohistochemistry and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. 2. Immunoblotting of extracts from freshly isolated myometrial tissue, affinity-enriched for NOS proteins by precipitation with ADP-sepharose, revealed expression of endothelial NOS (eNOS or NOS3) in tissues from preterm, term non-labour and active labour at term. Inducible NOS (iNOS or NOS2) and neuronal NOS (nNOS or NOS1) proteins were not detected at any stage of pregnancy. 3. Immunohistochemical detection showed that expression of eNOS protein was restricted to the endothelium of the myometrial vasculature, with no staining detected in myometrial smooth muscle cells. 4. Messenger RNA for all three NOS isoforms was detected, although iNOS and nNOS mRNAs were detectable only with high cycle number, implying a low copy number. 5. NOS isoforms were not detectable in human myometrial smooth muscle cells cultured from term non-labour pregnancies. Cytokine stimulation of cultured myometrial cells did not induce iNOS expression or nitrite accumulation in the culture medium, although both iNOS protein and nitrite release were detected in the human pulmonary epithelial cell line A549. 6. Levels of eNOS protein and of NOS mRNA expression were not correlated with gestational stage, suggesting that endogenously produced NO is not likely to be a modulator of myometrial tone during human pregnancy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endometrial and myometrial expression of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in pre- and postmenopausal women.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999 Jun;84(6):2226-32. doi: 10.1210/jcem.84.6.5759. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999. PMID: 10372735
-
Changes in expression of the nitric oxide synthase isoforms in rat uterus and cervix during pregnancy and parturition.Mol Hum Reprod. 1997 Nov;3(11):995-1003. doi: 10.1093/molehr/3.11.995. Mol Hum Reprod. 1997. PMID: 9433927
-
Characterization of the induction of nitric oxide synthase and cyclo-oxygenase in rat aorta in organ culture.Br J Pharmacol. 1997 May;121(1):125-33. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701100. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9146896 Free PMC article.
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS): More than an inducible enzyme? Rethinking the classification of NOS isoforms.Pharmacol Res. 2025 Jun;216:107781. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2025.107781. Epub 2025 May 17. Pharmacol Res. 2025. PMID: 40389042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitric oxide synthase: non-canonical expression patterns.Front Immunol. 2014 Oct 9;5:478. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00478. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25346730 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of calcium-calmodulin kinase restores nitric oxide production and signaling in submandibular glands of a mouse model of salivary dysfunction.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Dec;143(8):1058-65. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705952. Epub 2004 Nov 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15533891 Free PMC article.
-
Gasotransmitters in pregnancy: from conception to uterine involution.Biol Reprod. 2019 Jul 1;101(1):4-25. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioz038. Biol Reprod. 2019. PMID: 30848786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of the release of exogenous nitric oxide on the responses of the pregnant human myometrium to oxytocin.Dev Period Med. 2018;22(4):301-307. doi: 10.34763/devperiodmed.20182204.301307. Dev Period Med. 2018. PMID: 30636226 Free PMC article.
-
Anandamide induces sperm release from oviductal epithelia through nitric oxide pathway in bovines.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30671. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030671. Epub 2012 Feb 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22363468 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen-induced contraction of coronary arteries is mediated by superoxide generated in vascular smooth muscle.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005 Oct;289(4):H1468-75. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01173.2004. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16162867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartlett S, Sawdy R, Dennes W, Bennett P, Mann GE. Cytokine-induced regulation of nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase 2 in cultured human myometrial cells. Journal of the Society for Gynecologic Investigation. 1998;5:183A. abstract.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

