Penetration of rufloxacin into the cerebrospinal fluid in patients with inflamed and uninflamed meninges
- PMID: 10602726
- PMCID: PMC89631
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.44.1.73-77.2000
Penetration of rufloxacin into the cerebrospinal fluid in patients with inflamed and uninflamed meninges
Abstract
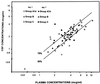
Forty-four patients scheduled for lumbar puncture (LP) were recruited to determine the level of penetration of orally administered rufloxacin into cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The patients were divided into three clinical groups: those with normal CSF (groups A(1d) and A(7d)), those with aseptic meningitis (group B), and those with bacterial meningitis (group C). Members of group A(1d) received a single 400-mg rufloxacin dose, while group A(7d), B, and C constituents had a multiple-dose regimen (one 400-mg dose, followed by one 200-mg dose daily for 6 days). LP was performed on group A(1d) members 5 h after they had received treatment, while for group A(7d) it was undertaken 5 h after administration of the last dose. For group B, LP was performed 5 h after the first and the last doses, whereas for group C it was undertaken after the first, fourth, and last doses. Concentrations of rufloxacin in simultaneously collected CSF and plasma samples were determined. Mean CSF/plasma rufloxacin concentration ratios ranged from 0.57 to 0.84, depending on the study group. A higher, but not statistically significant, degree of penetration into CSF was observed in patients with bacterial meningitis than in those with normal CSF or aseptic meningitis. These data indicate that rufloxacin diffuses efficiently into the CSF of patients with either inflamed or uninflamed meninges.
Figures
References
-
- Asuquo A E, Piddock L J V. Accumulation and killing kinetics of fifteen quinolones for Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1993;31:865–880. - PubMed
-
- Barling R W A, Selkon J B. The penetration of antibiotics into cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978;4:203–227. - PubMed
-
- Cogo R, Rimoldi R, Mattina R, Imbimbo B P. Steady-state pharmacokinetics of rufloxacin in elderly patients with lower respiratory tract infections. Ther Drug Monit. 1992;14:36–41. - PubMed
-
- Davey P G, McDonald T, Lindsay G. Post-marketing surveillance of quinolones 1988–1990. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991;10:384–389. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical