Strain-specific restriction of the antiphagocytic property of group A streptococcal M proteins
- PMID: 10603375
- PMCID: PMC97108
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.1.107-112.2000
Strain-specific restriction of the antiphagocytic property of group A streptococcal M proteins
Abstract
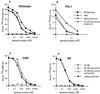
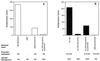
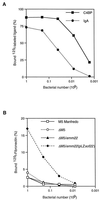
Group A streptococcal M proteins are type-specific virulence factors that inhibit phagocytosis. We used two M proteins, M5 and Emm22, to analyze the influence of genetic background on the properties of M proteins. Mutant strains, engineered to lack these M proteins, were complemented with genes encoding the homologous or heterologous M protein, and the complemented strains were analyzed for phagocytosis resistance. Neither the M5 nor the Emm22 protein conferred phagocytosis resistance in the heterologous background, but they did do so in the homologous background. This was not due to lack of surface expression in the heterologous background. Moreover, the M5 and Emm22 proteins expressed in heterologous background appeared to have normal structure, since they were not affected in their ability to bind different human plasma proteins. In particular, M5 or Emm22 had normal ability to bind human complement inhibitors, a property that has been implicated in phagocytosis resistance. Results similar to those obtained with M5 and Emm22 were obtained in experiments with the M6 and Emm4 proteins. Together, these data suggest that the surface expression of M protein alone may not be sufficient to confer phagocytosis resistance and consequently that strain-specific factors other than M and Emm proteins may contribute to the ability of group A streptococci to resist phagocytosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of two different antiphagocytic M proteins by Streptococcus pyogenes of the OF+ lineage.J Immunol. 1998 Jan 15;160(2):860-9. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9551922
-
Factor H binds to the hypervariable region of many Streptococcus pyogenes M proteins but does not promote phagocytosis resistance or acute virulence.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(4):e1003323. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003323. Epub 2013 Apr 18. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23637608 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of M49, Mrp, Enn, and C5a peptidase proteins on colonization of the mouse oral mucosa by Streptococcus pyogenes.Infect Immun. 1998 Nov;66(11):5399-405. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.11.5399-5405.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9784550 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of group A streptococcal infections.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2000 Jul;13(3):470-511. doi: 10.1128/CMR.13.3.470. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2000. PMID: 10885988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Group A streptococcal M proteins: virulence factors and protective antigens.Immunol Today. 1992 Sep;13(9):362-7. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90173-5. Immunol Today. 1992. PMID: 1281632 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationships between emm and multilocus sequence types within a global collection of Streptococcus pyogenes.BMC Microbiol. 2008 Apr 11;8:59. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-8-59. BMC Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18405369 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue tropisms in group A streptococcal infections.Future Microbiol. 2010 Apr;5(4):623-38. doi: 10.2217/fmb.10.28. Future Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20353302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adherence to and invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells are promoted by fibrinogen-binding protein FbsA of Streptococcus agalactiae.Infect Immun. 2005 Jul;73(7):4404-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.7.4404-4409.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15972538 Free PMC article.
-
Incremental Contributions of FbaA and Other Impetigo-Associated Surface Proteins to Fitness and Virulence of a Classical Group A Streptococcal Skin Strain.Infect Immun. 2017 Oct 18;85(11):e00374-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00374-17. Print 2017 Nov. Infect Immun. 2017. PMID: 28808160 Free PMC article.
-
The novel fibrinogen-binding protein FbsB promotes Streptococcus agalactiae invasion into epithelial cells.Infect Immun. 2004 Jun;72(6):3495-504. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.6.3495-3504.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15155657 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berge A, Björck L. Streptococcal cysteine proteinase releases biologically active fragments of streptococcal surface proteins. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:9862–9867. - PubMed
-
- Bisno A L, Stevens D L. Streptococcal infections of skin and soft tissues. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:240–245. - PubMed
-
- Caparon M G, Scott J R. Genetic manipulation of pathogenic streptococci. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:556–586. - PubMed
-
- Courtney H S, Hasty D L, Li Y, Chiang H C, Thacker J L, Dale J B. Serum opacity factor is a major fibronectin-binding protein and a virulence determinant of M type 2 Streptococcus pyogenes. Mol Microbiol. 1999;32:89–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

