Additive attenuation of virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae by mutation of the genes encoding pneumolysin and other putative pneumococcal virulence proteins
- PMID: 10603379
- PMCID: PMC97112
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.1.133-140.2000
Additive attenuation of virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae by mutation of the genes encoding pneumolysin and other putative pneumococcal virulence proteins
Abstract
Although the polysaccharide capsule of Streptococcus pneumoniae has been recognized as a sine qua non of virulence, much recent attention has focused on the role of pneumococcal proteins in pathogenesis, particularly in view of their potential as vaccine antigens. The individual contributions of pneumolysin (Ply), the major neuraminidase (NanA), autolysin (LytA), hyaluronidase (Hyl), pneumococcal surface protein A (PspA), and choline-binding protein A (CbpA) have been examined by specifically mutagenizing the respective genes in the pneumococcal chromosome and comparing the impact on virulence in a mouse intraperitoneal challenge model. Mutagenesis of either the ply, lytA, or pspA gene in S. pneumoniae D39 significantly reduced virulence, relative to that of the wild-type strain, indicating that the respective gene products contribute to pathogenesis. On the other hand, mutations in nanA, hyl, or cbpA had no significant impact. The virulence of D39 derivatives carrying a ply deletion mutation as well as an insertion-duplication mutation in one of the other genes was also examined. Mutagenesis of either nanA or lytA did not result in an additional attenuation of virulence in the ply deletion background. However, significant additive attenuation in virulence was observed for the strains with ply-hyl, ply-pspA, and ply-cbpA double mutations.
Figures


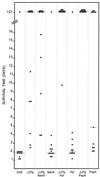

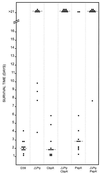

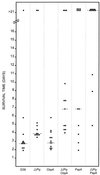
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

