Cytolethal distending toxin sequence and activity in the enterohepatic pathogen Helicobacter hepaticus
- PMID: 10603386
- PMCID: PMC97119
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.1.184-191.2000
Cytolethal distending toxin sequence and activity in the enterohepatic pathogen Helicobacter hepaticus
Abstract
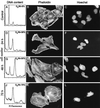
Little is known about the molecular pathogenesis of hepatitis and enterocolitis caused by enterohepatic Helicobacter species. Sonicates of the murine pathogen Helicobacter hepaticus were found to cause progressive cell distension, accumulation of filamentous actin, and G(2)/M cell cycle arrest in HeLa cell monolayers. The genes encoding this cytotoxic activity were cloned from H. hepaticus. Three open reading frames with closest homology to cdtA, cdtB, and cdtC from Campylobacter jejuni were identified. Sonicates of a laboratory strain of Escherichia coli carrying the cloned cdtABC gene cluster from H. hepaticus reproduced the cytotoxic activities seen with sonicates of H. hepaticus. Cytolethal distending toxin activity is a potential virulence determinant of H. hepaticus that may play a role in the pathogenesis of Helicobacter-associated hepatitis and enterocolitis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of cdtB homologues and cytolethal distending toxin activity in enterohepatic Helicobacter spp.J Med Microbiol. 2000 Jun;49(6):525-534. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-6-525. J Med Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10847206
-
Comparative analysis of cytolethal distending toxin (cdt) genes among Campylobacter jejuni, C. coli and C. fetus strains.Microb Pathog. 2007 May-Jun;42(5-6):174-83. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2007.01.005. Epub 2007 Feb 6. Microb Pathog. 2007. PMID: 17353111
-
Cytolethal distending toxin: a potential virulence factor for Helicobacter cinaedi.J Infect Dis. 2003 Dec 15;188(12):1892-7. doi: 10.1086/379837. Epub 2003 Dec 9. J Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 14673770
-
The contribution of cytolethal distending toxin to bacterial pathogenesis.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2006 Oct-Dec;32(4):227-48. doi: 10.1080/10408410601023557. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17123907 Review.
-
In vivo virulence properties of bacterial cytolethal-distending toxin.Cell Microbiol. 2008 Aug;10(8):1599-607. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01173.x. Epub 2008 May 16. Cell Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18489725 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of cholesterol on disease progression.Biomedicine (Taipei). 2015 Jun;5(2):7. doi: 10.7603/s40681-015-0007-8. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Biomedicine (Taipei). 2015. PMID: 26048694 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of KB and HEp-2 cell responses to an invasive, cytolethal distending toxin-producing strain of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans.Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2002 Aug;17(4):245-51. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-302x.2002.170407.x. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12121475 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella typhi encodes a functional cytolethal distending toxin that is delivered into host cells by a bacterial-internalization pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Mar 30;101(13):4614-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400932101. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15070766 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance of human periodontal ligament fibroblasts to the cytolethal distending toxin of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans.J Periodontol. 2005 Jul;76(7):1189-201. doi: 10.1902/jop.2005.76.7.1189. J Periodontol. 2005. PMID: 16018764 Free PMC article.
-
Functional studies of the recombinant subunits of a cytolethal distending holotoxin.Cell Microbiol. 2002 Apr;4(4):245-55. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2002.00186.x. Cell Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11952641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akopyants N S, Clifton S W, Kersulyte D, Crabtree J E, Youree B E, Reece C A, Bukanov N O, Drazek E S, Roe B A, Berg D E. Analyses of the cag pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori. Mol Microbiol. 1998;28:37–53. - PubMed
-
- Allos B M, Blaser M J. Campylobacter jejuni and the expanding spectrum of related infections. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;20:1092–1099. - PubMed
-
- Alm R A, Ling L S, Moir D T, King B L, Brown E D, Doig P C, Smith D R, Noonan B, Guild B C, deJonge B L, Carmel G, Tummino P J, Caruso A, Uria-Nickelsen M, Mills D M, Ives C, Gibson R, Merberg D, Mills S D, Jiang Q, Taylor D E, Vovis G F, Trust T J. Genomic-sequence comparison of two unrelated isolates of the human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature. 1999;397:176–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

