A P5 peptide that is homologous to peptide 10 of OprF from Pseudomonas aeruginosa enhances clearance of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae from acutely infected rat lung in the absence of detectable peptide-specific antibody
- PMID: 10603411
- PMCID: PMC97144
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.1.377-381.2000
A P5 peptide that is homologous to peptide 10 of OprF from Pseudomonas aeruginosa enhances clearance of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae from acutely infected rat lung in the absence of detectable peptide-specific antibody
Abstract
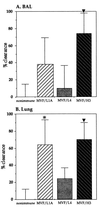
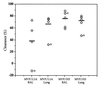
Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) is an opportunistic pathogen associated with otitis media and the exacerbation of chronic bronchitis. This study reports the vaccine potential of three peptides representing conserved regions of the NTHi P5 outer membrane protein which have been fused to a promiscuous measles virus F protein T-cell eptitope (MVF). The peptides correspond to a region in surface loop one (MVF/L1A), the central region of loop four (MVF/L4), and a C-terminal region homologous to peptide 10 of OprF from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MVF/H3). Immunization of rats with MVF/H3 was the most efficacious in significantly reducing the number of viable NTHi in both the broncho-alveolar lavage fluid (74%) and lung homogenates (70%), compared to control rats. Importantly, despite significantly increased rates of clearance, immunization with MVF/H3 elicited poor antibody responses, suggesting that cell-mediated rather than humoral responses play an important role in the enhanced clearance of NTHi in this model.
Figures

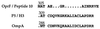
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of the 26-kilodalton outer membrane protein and two P5 fimbrin-derived immunogens to induce clearance of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae from the rat middle ear and lungs as well as from the chinchilla middle ear and nasopharynx.Infect Immun. 2003 Aug;71(8):4691-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.8.4691-4699.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12874350 Free PMC article.
-
Immunization with recombinant transferrin binding protein B enhances clearance of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae from the rat lung.Infect Immun. 1999 May;67(5):2138-44. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.5.2138-2144.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10225866 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced respiratory clearance of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae following mucosal immunization with P6 in a rat model.Infect Immun. 1995 Aug;63(8):2931-40. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.8.2931-2940.1995. Infect Immun. 1995. PMID: 7622215 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) vaccine.Vaccine. 2000 Dec 8;19 Suppl 1:S108-15. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(00)00288-7. Vaccine. 2000. PMID: 11163473 Review.
-
Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae as a pathogen in children.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009 Jan;28(1):43-8. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e318184dba2. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009. PMID: 19057458 Review.
Cited by
-
Epitope-specific immune recognition of the nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae outer membrane protein 26.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013 Mar;9(3):625-35. doi: 10.4161/hv.23255. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23292125 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of immunodominant and potentially protective epitopes of Mannheimia haemolytica serotype 1 outer membrane lipoprotein PlpE.Infect Immun. 2004 Dec;72(12):7265-74. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.12.7265-7274.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15557652 Free PMC article.
-
Genome sequencing of disease and carriage isolates of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae identifies discrete population structure.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Apr 8;111(14):5439-44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1403353111. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24706866 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of the 26-kilodalton outer membrane protein and two P5 fimbrin-derived immunogens to induce clearance of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae from the rat middle ear and lungs as well as from the chinchilla middle ear and nasopharynx.Infect Immun. 2003 Aug;71(8):4691-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.8.4691-4699.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12874350 Free PMC article.
-
Epitope mapping of the outer membrane protein P5-homologous fimbrin adhesin of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae.Infect Immun. 2000 Apr;68(4):2119-28. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.4.2119-2128.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10722609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bakaletz L O, Leake E R, Billy J M, Kaumaya P T P. Relative immunogenicity and efficacy of two synthetic chimeric peptides of fimbrin as vaccinogens against nasopharyngeal colonization by nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Vaccine. 1997;15:955–961. - PubMed
-
- Bakaletz L O, Kennedy B-J, Novotny L A, Duquesne G, Cohen J, Lobet Y. Protection against development of otitis media induced by nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae by both active and passive immunization in a chinchilla model of virus-bacterium superinfection. Infect Immun. 1999;67:2746–2762. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Constant S L, Bottomly K. Induction of Th1 and Th2 CD4+ T cell responses: the alternative approaches. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:297–322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

