ExoT of cytotoxic Pseudomonas aeruginosa prevents uptake by corneal epithelial cells
- PMID: 10603417
- PMCID: PMC97150
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.1.403-406.2000
ExoT of cytotoxic Pseudomonas aeruginosa prevents uptake by corneal epithelial cells
Abstract
The presence of invasion-inhibitory activity that is regulated by the transcriptional activator ExsA of cytotoxic Pseudomonas aeruginosa has previously been proposed. The results of this study show that both ExoT and ExoS, known type III secreted effector proteins of P. aeruginosa that are regulated by ExsA, possess this activity. Invasion was reduced 94.4% by ExoT and 96.0% by ExoS. Invasion-inhibitory activity is not linked to ADP-ribosylation activity, at least for ExoS, since a noncatalytic mutant also inhibits uptake by an epithelial cell line (invasion was reduced 96. 0% by ExoSE381A).
Figures
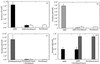
 ) (c).
PA103exoUexsA (█) did not inhibit invasion when
coincubated with 6294 (■) (d).
) (c).
PA103exoUexsA (█) did not inhibit invasion when
coincubated with 6294 (■) (d).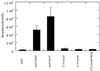
Similar articles
-
Mutation of lasA and lasB reduces Pseudomonas aeruginosa invasion of epithelial cells.Microbiology (Reading). 2003 Aug;149(Pt 8):2291-2299. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.26280-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2003. PMID: 12904569
-
Contribution of ExsA-regulated factors to corneal infection by cytotoxic and invasive Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a murine scarification model.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003 Sep;44(9):3892-8. doi: 10.1167/iovs.02-1302. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003. PMID: 12939306
-
ExoU expression by Pseudomonas aeruginosa correlates with acute cytotoxicity and epithelial injury.Mol Microbiol. 1997 Aug;25(3):547-57. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.4891851.x. Mol Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9302017
-
ExoU is a potent intracellular phospholipase.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Sep;53(5):1279-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04194.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15387809 Review.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa ExoS and ExoT.Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2004;152:79-92. doi: 10.1007/s10254-004-0031-7. Epub 2004 Aug 24. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15375697 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for intracellular Pseudomonas aeruginosa.J Bacteriol. 2024 May 23;206(5):e0010924. doi: 10.1128/jb.00109-24. Epub 2024 Apr 10. J Bacteriol. 2024. PMID: 38597609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa ExsA Regulates a Metalloprotease, ImpA, That Inhibits Phagocytosis of Macrophages.Infect Immun. 2019 Nov 18;87(12):e00695-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00695-19. Print 2019 Dec. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 31527124 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular mechanism of acute lung injury caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: from bacterial pathogenesis to host response.J Intensive Care. 2014 Feb 18;2(1):10. doi: 10.1186/2052-0492-2-10. eCollection 2014. J Intensive Care. 2014. PMID: 25520826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of the exoS gene and protein expression in soil and clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Infect Immun. 2001 Apr;69(4):2198-210. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.4.2198-2210.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11254575 Free PMC article.
-
Type III secretion phenotypes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains change during infection of individuals with cystic fibrosis.J Clin Microbiol. 2004 Nov;42(11):5229-37. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.11.5229-5237.2004. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15528719 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersson K, Carballeira N, Magnusson K-E, Persson C, Stendahl O, Wolf-Watz H, Fällman M. YopH of Yersinia pseudotuberculosisinterrupts early phosphotyrosine signaling associated with phagocytosis. Mol Microbiol. 1996;20:1057–1069. - PubMed
-
- Bölin I, Wolf-Watz H. The plasmid-encoded Yop2b protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosisis a virulence determinant regulated by calcium and temperature at the level of transcription. Mol Microbiol. 1988;2:237–245. - PubMed
-
- Cowell B A, Wu C, Fleiszig S M J. Use of an animal model in studies of bacterial corneal infection. Inst Lab Anim Res J. 1999;40:43–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

