Adrenaline-induced mobilization of T cells in HIV-infected patients
- PMID: 10606972
- PMCID: PMC1905544
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01102.x
Adrenaline-induced mobilization of T cells in HIV-infected patients
Abstract
The present study aimed to investigate lymphocyte mobilization from peripheral cell reservoirs in HIV-infected patients. Nine HIV-infected patients on stable highly active anti-retroviral therapy (HAART), eight treatment-naive HIV-infected patients and eight HIV- controls received a 1-h adrenaline infusion. The adrenaline infusion induced a three-fold increase in the concentration of lymphocytes in all three groups. All HIV-infected patients mobilized significantly higher numbers of CD8+ cells but less CD4+ cells. All subjects mobilized CD45RA+CD62L+ and CD8+CD28+ cells to a lesser extent than CD45RO+CD45RA- and CD8+CD28-cells. Furthermore, high numbers of CD8+CD38+ cells were mobilized only in the HIV-infected patients. It was therefore predominantly T cells with an activated phenotype which were mobilized after adrenaline stimulation. It is concluded that the HIV-associated immune defect induced an impaired ability to mobilize immune-competent cells in response to stress stimuli. Furthermore, the study does not support the idea that CD4+ T cells are trapped in lymph nodes by HIV antigens, because untreated and HAART-treated HIV-infected patients mobilized similar numbers of CD4+ T cells. Finally, no evidence was found for the existence of a HAART-induced non-circulating pool of CD4+ T cells.
Figures
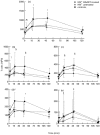
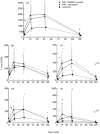

References
-
- Fauci AS, Pantaleo G, Stanley S, Weissman D. Immunopathogenic mechanisms of HIV infection. Ann Intern Med. 1996;124:654–63. - PubMed
-
- Miedema F. Immunological abnormalities in the natural history of HIV infection: mechanisms and clinical relevance. Immunodefic Rev. 1992;3:173–93. - PubMed
-
- Ho DD, Neumann AU, Perelson AS, Chen W, Leonard JM, Markowitz M. Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection. Nature. 1995;373:123–6. - PubMed
-
- Wei X, Ghosh SK, Taylor ME, et al. Viral dynamics in human immunedefiency virus type 1 infection. Nature. 1995;373:117–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

