The role of IL-12 in inflammatory activity of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- PMID: 10606980
- PMCID: PMC1905529
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01095.x
The role of IL-12 in inflammatory activity of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Erratum in
- Clin Exp Immunol 2000 Apr;120(1):224. Kim, WU [corrected to Kim, W]; Min SY [corrected to Min, S]; Cho, ML [corrected to Cho, M]; Min, DJ [corrected to Min, J]; Lee, SH [corrected to Lee, S]; Park, SH [corrected to Park, S]; Cho, CS [corrected to Cho, C]; Kim, HY [corrected to Kim, H]
Abstract
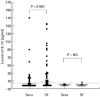
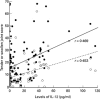
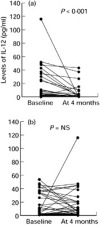
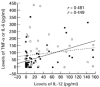
The aim of this study was to investigate the role of IL-12 in patients with RA. IL-12 (p70) and its associated cytokines were measured in sera and synovial fluid (SF) using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent method. Seven American College of Rheumatology (ACR) core set measures as well as IL-12 levels were sequentially monitored at the commencement and 4 months after treatment with a low-dose steroid and disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs). In sera, 64 (42.2%) of 152 RA patients had detectable concentrations of IL-12 (p70), whereas one (1.4%) of 69 osteoarthritis (OA) patients and five (10%) of 50 healthy controls had detectable IL-12 (P < 0.001). The median level of circulating IL-12 was also higher in RA patients (P < 0.001). In SF, the number of patients with detectable IL-12 and the median IL-12 levels were significantly higher in RA patients (n = 53) than in OA patients (n = 22). In paired samples (n = 53) of sera and SF from RA patients, IL-12 levels were higher in the SF than in sera (P < 0.001). Patients with detectable IL-12 (n = 51) in sera had higher tender joint scores (P = 0.003), swollen joint scores (P < 0.001) and C-reactive protein (CRP; P = 0.036), than those without (n = 55). Four months after treatment with DMARDs, the improved group showed a larger IL-12 decrease than the non-improved group (P = 0.017). The levels of IL-12 correlated positively with those of IL-2, interferon-gamma, IL-6, and tumour necrosis factor-alpha, but were correlated inversely with those of IL-10. Our results demonstrate that IL-12 levels reflect RA disease activity and that IL-12 is involved in the production of proinflammatory cytokines. An IL-12 blockade could be useful for the treatment of RA.
Figures
References
-
- Brennan FM, Maini RN, Feldmann M. TNF-alpha: pivotal role in rheumatoid arthritis? Br J Rheumatol. 1992;31:293–8. - PubMed
-
- Ito A, Itoh Y, Sasaguri Y, Morimatsu M, Mori Y. Effects of interleukin-6 on the metabolism of connective tissue components in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 1992;35:1197–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

