A locus and mechanism of action for associative morphine tolerance
- PMID: 10607394
- PMCID: PMC4327857
- DOI: 10.1038/71120
A locus and mechanism of action for associative morphine tolerance
Abstract
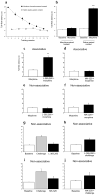
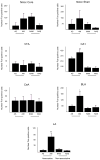
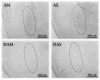
Repeated administration of an opioid in the presence of specific environmental cues can induce tolerance specific to that setting (associative tolerance). Prolonged or repeated administration of an opioid without consistent contextual pairing yields non-associative tolerance. Here we demonstrate that cholecystokinin acting at the cholecystokinin-B receptor is required for associative but not non-associative morphine tolerance. Morphine given in the morphine-associated context increased Fos-like immunoreactivity in the lateral amygdala and hippocampal area CA1. Microinjection of the cholecystokinin B antagonist L-365,260 into the amygdala blocked associative tolerance. These results indicate that cholecystokinin acting in the amygdala is necessary for associative tolerance to morphine's analgesic effect.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cholecystokinin receptor mechanism(s) and morphine tolerance in mice.Pharmacol Toxicol. 1999 Jan;84(1):46-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1999.tb02110.x. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1999. PMID: 9974190
-
Caerulein may potentiate morphine-induced antinociception by cholecystokinin-A and/or cholecystokinin-B receptor mechanisms.Gen Pharmacol. 1997 Feb;28(2):337-40. doi: 10.1016/s0306-3623(96)00157-7. Gen Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9013214
-
Cholecystokinin-B receptor antagonists attenuate morphine dependence and withdrawal in rats.Neuroreport. 2000 Mar 20;11(4):829-32. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200003200-00034. Neuroreport. 2000. PMID: 10757528
-
Involvement of local cholecystokinin in the tolerance induced by morphine microinjections into the periaqueductal gray of rats.Pain. 2003 Mar;102(1-2):9-16. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3959(02)00153-7. Pain. 2003. PMID: 12620592
-
Reactivation of cocaine conditioned place preference induced by stress is reversed by cholecystokinin-B receptors antagonist in rats.Brain Res. 2002 Nov 1;954(1):132-40. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(02)03359-0. Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12393241
Cited by
-
G-protein receptor kinase 3 (GRK3) influences opioid analgesic tolerance but not opioid withdrawal.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Jan;141(1):55-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705595. Epub 2003 Dec 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 14662727 Free PMC article.
-
Methadone: a new old drug with promises and pitfalls.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2009 Feb;13(1):24-30. doi: 10.1007/s11916-009-0006-0. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2009. PMID: 19126367 Review.
-
MicroRNAs Are Involved in the Development of Morphine-Induced Analgesic Tolerance and Regulate Functionally Relevant Changes in Serpini1.Front Mol Neurosci. 2016 Mar 24;9:20. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00020. eCollection 2016. Front Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27047334 Free PMC article.
-
Conditioned morphine tolerance promotes neurogenesis, dendritic remodelling and pro-plasticity molecules in the adult rat hippocampus.Addict Biol. 2024 Mar;29(3):e13377. doi: 10.1111/adb.13377. Addict Biol. 2024. PMID: 38506630 Free PMC article.
-
Role of protein kinase C and mu-opioid receptor (MOPr) desensitization in tolerance to morphine in rat locus coeruleus neurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2009 Jan;29(2):307-18. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06573.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19200236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Faris PL, Komisaruk BR, Watkins LR, Mayer DJ. Evidence for the neuropeptide cholecystokinin as an antagonist of opiate analgesia. Science. 1983;219:310–312. - PubMed
-
- Magnuson DS, Sullivan AF, Simonnet G, Roques BP, Dickenson AH. Differential interactions of cholecystokinin and FLFQPQRF-NH2 with mu and delta opioid antinociception in the rat spinal cord. Neuropeptides. 1990;16:213–218. - PubMed
-
- Watkins LR, Kinscheck IB, Mayer DJ. Potentiation of opiate analgesia and apparent reversal of morphine tolerance by proglumide. Science. 1984;224:395–396. - PubMed
-
- Katsuura G, Itoh S. Potentiation of β-endorphin effects by proglumide in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985;107:363–366. - PubMed
-
- Dourish CT, et al. The selective CCK-B receptor antagonist L–365,260 enhances morphine analgesia and prevents morphine tolerance in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990;176:35–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

