Macrophage-tumour cell interactions: identification of MUC1 on breast cancer cells as a potential counter-receptor for the macrophage-restricted receptor, sialoadhesin
- PMID: 10610356
- PMCID: PMC2326916
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00827.x
Macrophage-tumour cell interactions: identification of MUC1 on breast cancer cells as a potential counter-receptor for the macrophage-restricted receptor, sialoadhesin
Abstract
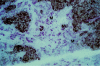
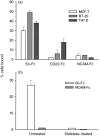
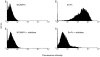
In many carcinomas, infiltrating macrophages are commonly found closely associated with tumour cells but little is known concerning the nature or significance of adhesion molecules involved in these cellular interactions. Here we demonstrate in primary human breast cancers that sialoadhesin (Sn), a macrophage-restricted adhesion molecule, is frequently expressed on infiltrating cells that often make close contact with breast carcinoma cells. To determine whether Sn could act as a specific receptor for ligands on breast cancer cell lines, binding assays were performed with a recombinant form of the protein fused to the Fc portion of human immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) (Sn-Fc). Sn-Fc was found to bind specifically and in a sialic acid-dependent manner to the breast cancer cell lines MCF-7, T47.D and BT-20 both in solid- and solution-phase binding assays. To investigate the nature of the sialoglycoproteins recognized by Sn on breast cancer cells, MCF-7 cells were labelled with [6-3H]glucosamine. Following precipitation with Sn-Fc, a major band of approximately 240000 MW was revealed, which was shown in reprecipitation and Western blotting experiments to be the epithelial mucin, MUC1.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sialoadhesin on macrophages: its identification as a lymphocyte adhesion molecule.J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):647-55. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.647. J Exp Med. 1992. PMID: 1512534 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of human sialoadhesin, a sialic acid binding receptor expressed by resident and inflammatory macrophage populations.Blood. 2001 Jan 1;97(1):288-96. doi: 10.1182/blood.v97.1.288. Blood. 2001. PMID: 11133773
-
Sialic acid binding receptors (siglecs) expressed by macrophages.J Leukoc Biol. 1999 Nov;66(5):705-11. doi: 10.1002/jlb.66.5.705. J Leukoc Biol. 1999. PMID: 10577497 Review.
-
Cutting edge: CD43 functions as a T cell counterreceptor for the macrophage adhesion receptor sialoadhesin (Siglec-1).J Immunol. 2001 Mar 15;166(6):3637-40. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.6.3637. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11238599
-
The potential role of sialoadhesin as a macrophage recognition molecule in health and disease.Glycoconj J. 1997 Aug;14(5):601-9. doi: 10.1023/a:1018588526788. Glycoconj J. 1997. PMID: 9298693 Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple changes in sialic acid biology during human evolution.Glycoconj J. 2009 Apr;26(3):231-45. doi: 10.1007/s10719-008-9183-z. Epub 2008 Sep 7. Glycoconj J. 2009. PMID: 18777136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomaterials for modulating innate immune cells in cancer immunotherapy.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2019 Jan;14(1):16-29. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2018.07.003. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2019. PMID: 32104435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination immunotherapy of chlorogenic acid liposomes modified with sialic acid and PD-1 blockers effectively enhances the anti-tumor immune response and therapeutic effects.Drug Deliv. 2021 Dec;28(1):1849-1860. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.1971797. Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 34515617 Free PMC article.
-
The inhibitory potencies of monoclonal antibodies to the macrophage adhesion molecule sialoadhesin are greatly increased following PEGylation.Bioconjug Chem. 2008 Oct;19(10):2088-94. doi: 10.1021/bc800259z. Epub 2008 Sep 23. Bioconjug Chem. 2008. PMID: 18808170 Free PMC article.
-
Non-invasive molecular imaging of inflammatory macrophages in allograft rejection.EJNMMI Res. 2015 Dec;5(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s13550-015-0146-7. Epub 2015 Nov 26. EJNMMI Res. 2015. PMID: 26611870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O’sullivan C, Lewis CE. Tumour-associated leucocytes: friends or foes in breast carcinoma. J Pathol. 1994;172:229. - PubMed
-
- O’Sullivan C, Lewis CE, Harris AL, Mcgee JO. Secretion of epidermal growth factor by macrophages associated with breast carcinoma. Lancet. 1993;342:148. - PubMed
-
- Lewis CE, Leek R, Harris A, Mcgee JO. Cytokine regulation of angiogenesis in breast cancer: the role of tumor-associated macrophages. J Leukocyte Biol. 1995;57:747. - PubMed
-
- Leek RD, Lewis CE, Whitehouse R, Greenall M, Clarke J, Harris AL. Association of macrophage infiltration with angiogenesis and prognosis in invasive breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1996;56:4625. - PubMed
-
- Mantovani A, Bottazzi B, Colotta F, Sozzani S, Ruco L. The origin and function of tumor-associated macrophages. Immunol Today. 1992;13:265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

