Cyclin D1 is required for transformation by activated Neu and is induced through an E2F-dependent signaling pathway
- PMID: 10611246
- PMCID: PMC85165
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.2.672-683.2000
Cyclin D1 is required for transformation by activated Neu and is induced through an E2F-dependent signaling pathway
Abstract
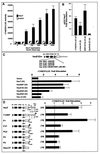
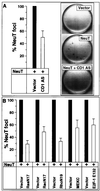
The neu (c-erbB-2) proto-oncogene encodes a tyrosine kinase receptor that is overexpressed in 20 to 30% of human breast tumors. Herein, cyclin D1 protein levels were increased in mammary tumors induced by overexpression of wild-type Neu or activating mutants of Neu in transgenic mice and in MCF7 cells overexpressing transforming Neu. Analyses of 12 Neu mutants in MCF7 cells indicated important roles for specific C-terminal autophosphorylation sites and the extracellular domain in cyclin D1 promoter activation. Induction of cyclin D1 by NeuT involved Ras, Rac, Rho, extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38, but not phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. NeuT induction of the cyclin D1 promoter required the E2F and Sp1 DNA binding sites and was inhibited by dominant negative E2F-1 or DP-1. Neu-induced transformation was inhibited by a cyclin D1 antisense or dominant negative E2F-1 construct in Rat-1 cells. Growth of NeuT-transformed mammary adenocarcinoma cells in nude mice was blocked by the cyclin D1 antisense construct. These results demonstrate that E2F-1 mediates a Neu-signaling cascade to cyclin D1 and identify cyclin D1 as a critical downstream target of neu-induced transformation.
Figures

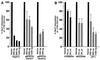




Similar articles
-
Inhibition of cyclin D1 kinase activity is associated with E2F-mediated inhibition of cyclin D1 promoter activity through E2F and Sp1.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Jun;18(6):3212-22. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.6.3212. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9584162 Free PMC article.
-
PIN1 is an E2F target gene essential for Neu/Ras-induced transformation of mammary epithelial cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Aug;22(15):5281-95. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.15.5281-5295.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12101225 Free PMC article.
-
pp60(v-src) induction of cyclin D1 requires collaborative interactions between the extracellular signal-regulated kinase, p38, and Jun kinase pathways. A role for cAMP response element-binding protein and activating transcription factor-2 in pp60(v-src) signaling in breast cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 1999 Mar 12;274(11):7341-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.11.7341. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10066798
-
Cyclins: roles in mitogenic signaling and oncogenic transformation.Growth Factors. 2006 Mar;24(1):13-9. doi: 10.1080/08977190500361812. Growth Factors. 2006. PMID: 16393691 Review.
-
Oncogenic and tumor-suppressive mouse models for breast cancer engaging HER2/neu.Int J Cancer. 2017 Feb 1;140(3):495-503. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30399. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Int J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 27553713 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of cyclin D1 expression by androgen receptor in breast cancer cells--identification of a novel androgen response element.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Sep;38(16):5351-65. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq278. Epub 2010 Apr 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20421209 Free PMC article.
-
Genes involved in breast cancer progression: analysis of global changes in gene expression or retroviral tagging?Am J Pathol. 2002 Dec;161(6):1973-7. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64473-2. Am J Pathol. 2002. PMID: 12466111 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands inhibit igf-ii and adipokine stimulated breast cancer cell proliferation.ISRN Endocrinol. 2013 Sep 23;2013:104850. doi: 10.1155/2013/104850. eCollection 2013. ISRN Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 24171117 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin D1 in Cancer: A Molecular Connection for Cell Cycle Control, Adhesion and Invasion in Tumor and Stroma.Cells. 2020 Dec 9;9(12):2648. doi: 10.3390/cells9122648. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33317149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of cyclin D1 transcription and CDK2 activity by Notch(ic): implication for cell cycle disruption in transformation by Notch(ic).Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Sep;21(17):5925-34. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.17.5925-5934.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11486031 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albanese C, Johnson J, Watanabe G, Eklund N, Vu D, Arnold A, Pestell R G. Transforming p21ras mutants and c-Ets-2 activate the cyclin D1 promoter through distinguishable regions. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:23589–23597. - PubMed
-
- Alberts A S, Geneste O, Treisman R. Activation of SRF-regulated chromosomal templates by Rho-family GTPases requires a signal that also induces H4 hyperacetylation. Cell. 1998;92:475–487. - PubMed
-
- Alessi D R, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley D T, Saltiel A R. PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27489–27494. - PubMed
-
- Amundadottir L T, Leder P. Signal transduction pathways activated and required for mammary carcinogenesis in response to specific oncogenes. Oncogene. 1998;16:737–746. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
