Synthetic genes for glycoprotein design and the elucidation of hydroxyproline-O-glycosylation codes
- PMID: 10611282
- PMCID: PMC24717
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.26.14736
Synthetic genes for glycoprotein design and the elucidation of hydroxyproline-O-glycosylation codes
Abstract
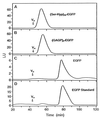
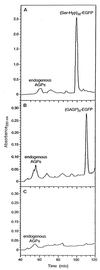
Design of hydroxyproline (Hyp)-rich glycoproteins (HRGPs) offers an approach for the structural and functional analysis of these wall components, which are broadly implicated in plant growth and development. HRGPs consist of multiple small repetitive "glycomodules" extensively O-glycosylated through the Hyp residues. The patterns of Hyp-O-glycosylation are putatively coded by the primary sequence as described by the Hyp contiguity hypothesis, which predicts contiguous Hyp residues to be attachment sites of small arabinooligosaccharides (1-5 Ara residues/Hyp); while clustered, noncontiguous Hyp residues are sites of arabinogalactan polysaccharide attachment. As a test, we designed two simple HRGPs as fusion proteins with green fluorescent protein. The first was a repetitive Ser-Hyp motif that encoded only clustered noncontiguous Hyp residues, predicted polysaccharide addition sites. The resulting glycoprotein had arabinogalactan polysaccharide O-linked to all Hyp residues. The second construct, based on the consensus sequence of a gum arabic HRGP, contained both arabinogalactan and arabinooligosaccharide addition sites and, as predicted, gave a product that contained both saccharide types. These results identify an O-glycosylation code of plants.
Figures


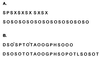
Similar articles
-
Glycosylation motifs that direct arabinogalactan addition to arabinogalactan-proteins.Plant Physiol. 2003 Jul;132(3):1362-9. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.021766. Plant Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12857818 Free PMC article.
-
Contiguous hydroxyproline residues direct hydroxyproline arabinosylation in Nicotiana tabacum.J Biol Chem. 2001 Apr 6;276(14):11272-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M011323200. Epub 2001 Jan 11. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11154705
-
Tomato LeAGP-1 arabinogalactan-protein purified from transgenic tobacco corroborates the Hyp contiguity hypothesis.Plant J. 2002 Aug;31(4):431-44. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01365.x. Plant J. 2002. PMID: 12182702
-
Synthetic genes for the elucidation of glycosylation codes for arabinogalactan-proteins and other hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001 Sep;58(10):1386-98. doi: 10.1007/PL00000783. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001. PMID: 11693521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extensin: repetitive motifs, functional sites, post-translational codes, and phylogeny.Plant J. 1994 Feb;5(2):157-72. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1994.05020157.x. Plant J. 1994. PMID: 8148875 Review.
Cited by
-
Glycosylation motifs that direct arabinogalactan addition to arabinogalactan-proteins.Plant Physiol. 2003 Jul;132(3):1362-9. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.021766. Plant Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12857818 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced secretion of human α1-antitrypsin expressed with a novel glycosylation module in tobacco BY-2 cell culture.Bioengineered. 2019 Dec;10(1):87-97. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2019.1604037. Bioengineered. 2019. PMID: 30957636 Free PMC article.
-
Three Decades of Advances in Arabinogalactan-Protein Biosynthesis.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Dec 15;11:610377. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.610377. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33384708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Hydroxyproline-Containing Proteins and Hydroxylation of Proline Residues in Rice.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Aug 7;11:1207. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01207. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32849749 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins in Arabidopsis. A genomic analysis.Plant Physiol. 2002 Jun;129(2):486-99. doi: 10.1104/pp.010884. Plant Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12068095 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

