MEKK1 suppresses oxidative stress-induced apoptosis of embryonic stem cell-derived cardiac myocytes
- PMID: 10611349
- PMCID: PMC24784
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.26.15127
MEKK1 suppresses oxidative stress-induced apoptosis of embryonic stem cell-derived cardiac myocytes
Abstract
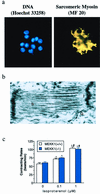
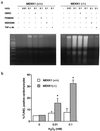
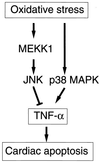
A combination of in vitro embryonic stem (ES) cell differentiation and targeted gene disruption has defined complex regulatory events underlying oxidative stress-induced cardiac apoptosis, a model of postischemic reperfusion injury of myocardium. ES cell-derived cardiac myocytes (ESCM) having targeted disruption of the MEKK1 gene were extremely sensitive, relative to wild-type ESCM, to hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis. In response to oxidative stress, MEKK1-/- ESCM failed to activate c-Jun kinase (JNK) but did activate p38 kinase similar to that observed in wild-type ESCM. The increased apoptosis was mediated through enhanced tumor necrosis factor alpha production, a response that was positively and negatively regulated by p38 and the MEKK1-JNK pathway, respectively. Thus, MEKK1 functions in the survival of cardiac myocytes by inhibiting the production of a proapoptotic cytokine. MEKK1 regulation of the JNK pathway is a critical response for the protection against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in cardiac myocytes.
Figures


References
-
- Lucchesi B R. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:561–576. - PubMed
-
- Werns S W, Lucchesi B R. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990;11:161–166. - PubMed
-
- McCord J M. Fed Proc. 1987;46:2402–2406. - PubMed
-
- Meldrum D R, Dinarello C A, Cleveland J C, Jr, Cain B S, Shames B D, Meng X, Harken A H. Surgery. 1998;124:291–296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

