Thalamocortical dysrhythmia: A neurological and neuropsychiatric syndrome characterized by magnetoencephalography
- PMID: 10611366
- PMCID: PMC24801
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.26.15222
Thalamocortical dysrhythmia: A neurological and neuropsychiatric syndrome characterized by magnetoencephalography
Abstract
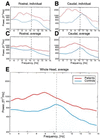
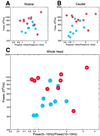
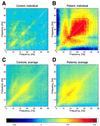
Spontaneous magnetoencephalographic activity was recorded in awake, healthy human controls and in patients suffering from neurogenic pain, tinnitus, Parkinson's disease, or depression. Compared with controls, patients showed increased low-frequency theta rhythmicity, in conjunction with a widespread and marked increase of coherence among high- and low-frequency oscillations. These data indicate the presence of a thalamocortical dysrhythmia, which we propose is responsible for all the above mentioned conditions. This coherent theta activity, the result of a resonant interaction between thalamus and cortex, is due to the generation of low-threshold calcium spike bursts by thalamic cells. The presence of these bursts is directly related to thalamic cell hyperpolarization, brought about by either excess inhibition or disfacilitation. The emergence of positive clinical symptoms is viewed as resulting from ectopic gamma-band activation, which we refer to as the "edge effect." This effect is observable as increased coherence between low- and high-frequency oscillations, probably resulting from inhibitory asymmetry between high- and low-frequency thalamocortical modules at the cortical level.
Figures
References
-
- Llinás R. Science. 1988;242:1654–1664. - PubMed
-
- Llinás R, Ribary U, Joliot M, Wang X J. In: Temporal Coding in the Brain. Buzsaki G, Llinás R, Singer W, Berthoz A, Christen Y, editors. Berlin: Springer; 1994. pp. 251–272.
-
- von der Marlsburg C. Internal Report. Göttingen, Germany: Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry; 1981.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

