Extensive conservation of sex chromosome organization between cat and human revealed by parallel radiation hybrid mapping
- PMID: 10613845
- PMCID: PMC311008
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.9.12.1223
Extensive conservation of sex chromosome organization between cat and human revealed by parallel radiation hybrid mapping
Abstract
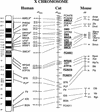
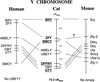
A radiation hybrid (RH)-derived physical map of 25 markers on the feline X chromosome (including 19 Type I coding loci and 6 Type II microsatellite markers) was compared to homologous marker order on the human and mouse X chromosome maps. Complete conservation of synteny and marker order was observed between feline and human X chromosomes, whereas the same markers identified a minimum of seven rearranged syntenic segments between mouse and cat/human X chromosome marker order. Within the blocks, the feline, human, and mouse marker order was strongly conserved. Similarly, Y chromosome locus order was remarkably conserved between cat and human Y chromosomes, with only one marker (SMCY) position rearranged between the species. Tight linkage and a conserved gene order for a segment encoding three genes, DFFRY-DBY-UTY in human, mouse, and cat Y chromosomes, coupled with demonstrated deletion effects of these genes on reproductive impairment in both human and mouse, implicates the region as critical for Y-mediated sperm production.
Figures
References
-
- Affara N, Bishop C, Brown W, Cooke H, Davey P, Ellis N, Graves JM, Jones M, Mitchell M, Rappold G, Tyler-Smith C, Yen P, Lau Y-FC. Report on the second international workshop on Y chromosome mapping 1995. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1996;73:33–76. - PubMed
-
- Archidiacono N, Storlazzi CT, Spalluto C, Ricco AS, Marzella R, Rocchi M. Evolution of chromosome Y in primates. Chromosoma. 1998;107:241–246. - PubMed
-
- Boehnke M. Multipoint analysis for radiation hybrid mapping. Ann Med. 1992;24:383–386. - PubMed
-
- Carver EA, Stubbs L. Zooming in on the human–mouse comparative map: Genome conservation re-examined on a high-resolution scale. Genome Res. 1997;7:1123–1137. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z-Q, Lautenberger JA, Lyons LA, McKenzie L, O'Brien SJ. A human genome map of comparative anchor tagged sequences. J Hered. 1999;90:477–484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
