The eps15 homology (EH) domain-based interaction between eps15 and hrb connects the molecular machinery of endocytosis to that of nucleocytosolic transport
- PMID: 10613896
- PMCID: PMC2174238
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.147.7.1379
The eps15 homology (EH) domain-based interaction between eps15 and hrb connects the molecular machinery of endocytosis to that of nucleocytosolic transport
Abstract
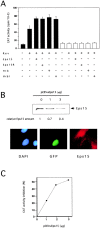
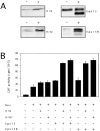
The Eps15 homology (EH) module is a protein-protein interaction domain that establishes a network of connections involved in various aspects of endocytosis and sorting. The finding that EH-containing proteins bind to Hrb (a cellular cofactor of the Rev protein) and to the related protein Hrbl raised the possibility that the EH network might also influence the so-called Rev export pathway, which mediates nucleocytoplasmic transfer of proteins and RNAs. In this study, we demonstrate that Eps15 and Eps15R, two EH-containing proteins, synergize with Hrb and Hrbl to enhance the function of Rev in the export pathway. In addition, the EH-mediated association between Eps15 and Hrb is required for the synergistic effect. The interaction between Eps15 and Hrb occurs in the cytoplasm, thus pointing to an unexpected site of action of Hrb, and to a possible role of the Eps15-Hrb complex in regulating the stability of Rev.
Figures



References
-
- Bogerd H.P., Fridell R.A., Madore S., Cullen B.R. Identification of a novel cellular cofactor for the Rev/Rex class of retroviral regulatory proteins. Cell. 1995;82:485–494. - PubMed
-
- Coda L., Salcini A.E., Confalonieri S., Pelicci G., Sorkina T., Sorkin A., Pelicci P.G., Di Fiore P.P. Eps15R is a tyrosine kinase substrate with characteristics of a docking protein possibly involved in coated pits-mediated internalization. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:3003–3012. - PubMed
-
- Cullen B.R. HIV-1 auxiliary proteinsmaking connections in a dying cell. Cell. 1998;93:685–692. - PubMed
-
- Fischer U., Huber J., Boelens W.C., Mattaj I.W., Luhrmann R. The HIV-1 Rev activation domain is a nuclear export signal that accesses an export pathway used by specific cellular RNAs. Cell. 1995;82:475–483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

