RNA-binding proteins TIA-1 and TIAR link the phosphorylation of eIF-2 alpha to the assembly of mammalian stress granules
- PMID: 10613902
- PMCID: PMC2174242
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.147.7.1431
RNA-binding proteins TIA-1 and TIAR link the phosphorylation of eIF-2 alpha to the assembly of mammalian stress granules
Abstract
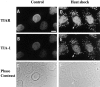
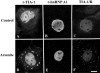
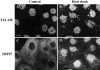
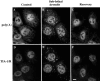
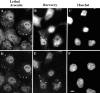
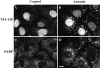
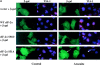
In response to environmental stress, the related RNA-binding proteins TIA-1 and TIAR colocalize with poly(A)(+) RNA at cytoplasmic foci that resemble the stress granules (SGs) that harbor untranslated mRNAs in heat shocked plant cells (Nover et al. 1989; Nover et al. 1983; Scharf et al. 1998). The accumulation of untranslated mRNA at SGs is reversible in cells that recover from a sublethal stress, but irreversible in cells subjected to a lethal stress. We have found that the assembly of TIA-1/R(+) SGs is initiated by the phosphorylation of eIF-2alpha. A phosphomimetic eIF-2alpha mutant (S51D) induces the assembly of SGs, whereas a nonphosphorylatable eIF-2alpha mutant (S51A) prevents the assembly of SGs. The ability of a TIA-1 mutant lacking its RNA-binding domains to function as a transdominant inhibitor of SG formation suggests that this RNA-binding protein acts downstream of the phosphorylation of eIF-2alpha to promote the sequestration of untranslated mRNAs at SGs. The assembly and disassembly of SGs could regulate the duration of stress- induced translational arrest in cells recovering from environmental stress.
Figures
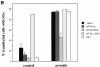

References
-
- Antic D., Keene J. Messenger RNP complexes containing human ELAV proteinsinteractions with cytoskeleton and translational apparatus. J. Cell Sci. 1998;111:183–197. - PubMed
-
- Berlanga J., Herrero S., De Haro C. Characterization of the hemin-sensitive eukaryotic initiation factor 2a kinase from mouse nonerythroid cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:32340–32346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

