The lipid-protein interface of a Shaker K(+) channel
- PMID: 10613918
- PMCID: PMC1887780
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.115.1.51
The lipid-protein interface of a Shaker K(+) channel
Abstract
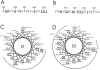
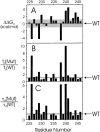
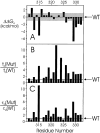
Tryptophan-substitution mutagenesis was applied to the first and third transmembrane segments (S1 and S3) of a Shaker-type K(+) channel for the purpose of ascertaining whether these sequences are alpha-helical. Point mutants were examined for significant functional changes, indicated by the voltage-activation curves and gating kinetics. Helical periodicity of functional alteration was observed throughout the entire S1 segment. A similar result was obtained with the first 14 residues of S3, but this periodicity disappeared towards the extracellular side of this transmembrane sequence. In both helical stretches, tryptophan-tolerant positions are clustered on approximately half the alpha-helix surface, as if the sidechains are exposed to the hydrocarbon region of the lipid bilayer. These results, combined with an analogous study of S2 (Monks, S., D.J. Needleman, and C. Miller. 1999. J. Gen. Physiol. 113:415-423), locate S1, S2, and S3 on the lipid-facing periphery of K(v) channels.
Figures






Comment in
-
Structure and packing orientation of transmembrane segments in voltage-dependent channels. Lessons from perturbation analysis.J Gen Physiol. 2000 Jan;115(1):29-32. doi: 10.1085/jgp.115.1.29. J Gen Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10613916 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Baldwin J.M., Schertler G.F.X., Unger V.M. An alpha-carbon template for the transmembrane helices in the rhodopsin family of G-protein–coupled receptors. J. Mol. Biol. 1997;272:144–164. - PubMed
-
- Doyle D.A., Cabral J.M., Pfuetzner R.A., Kuo A., Gulbis J.M., Cohen S.L., Chait B.T., MacKinnon R. The structure of the K+ channelmolecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science. 1998;280:69–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

