Characterization of Streptococcus agalactiae isolates of bovine and human origin by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis
- PMID: 10618066
- PMCID: PMC86023
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.1.71-78.2000
Characterization of Streptococcus agalactiae isolates of bovine and human origin by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis
Abstract
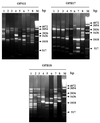
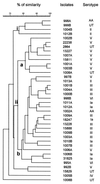
Streptococcus agalactiae is considered one of the major causes of bovine intramammary infections. It is also found in the vaginas of women without any apparent clinical symptoms, but reports of neonatal infections, causing significant morbidity, are relatively frequent. The aim of this study was to evaluate the genetic diversity of S. agalactiae strains isolated from bovine milk and from asymptomatic women in Québec, Canada, by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis. A total of 185 bovine isolates and 38 human isolates were first serotyped for capsular polysaccharide by double diffusion in agarose gel (bovine isolates) and coagglutination (human isolates). Strains were then studied by RAPD using 3 primers, designated OPS11, OPB17, and OPB18, which were selected from 12 primers. Thirty-eight percent of bovine isolates and 82% of human isolates could be serotyped. Prevalent serotypes were type III (28%) for bovine isolates and types V (26%) and III (24%) for human isolates. RAPD results showed that, taken together, all isolates (of bovine and human origin) shared 58% similarity. Ninety-four percent of these isolates were clustered in four groups (I, II, III, and IV) with 70% similarity among them. Three clusters, A (48 isolates), B (14 isolates), and C (32 isolates), with 79 to 80% similarity were identified within group IV, whereas the three other groups did not present any clusters. Despite some clustering of human isolates, relatively high diversity was seen among them. Relatively high heterogeneity was observed with the RAPD profiles, not only for field strains belonging to different serotypes but also for those within a given serotype.
Figures


References
-
- Baseggio N, Mansell P D, Browning J W, Browning G F. Strain differentiation of isolates of streptococci from bovine mastitis by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Mol Cell Probes. 1997;11:349–354. - PubMed
-
- Bingen E, Denamur E, Lambert-Zechovsky N, Aujard Y, Brahimi N, Geslin P, Elion J. Analysis of DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism extends the evidence for breast milk transmission in Streptococcus agalactiae late-onset neonatal infection. J Infect Dis. 1992;165:569–573. - PubMed
-
- Blumberg H M, Stephens D S, Licitra C, Pigott N, Facklam R, Swaminathan B, Wachsmuth I K. Molecular epidemiology of group B streptococcal infections: use of restriction endonuclease analysis of chromosomal DNA and DNA restriction fragment length polymorphisms of ribosomal RNA genes (ribotyping) J Infect Dis. 1992;166:574–579. - PubMed
-
- Bopp V, Lammler C. Comparative studies on group-B streptococci isolated from bovine milk samples in Thuringia and Hesse. Zentbl Veterinarmed B. 1995;42:427–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

