Serodiagnosis of recently acquired Toxoplasma gondii infection with a recombinant antigen
- PMID: 10618084
- PMCID: PMC88692
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.1.179-184.2000
Serodiagnosis of recently acquired Toxoplasma gondii infection with a recombinant antigen
Abstract
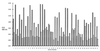
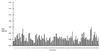
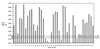
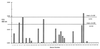
A portion of a cDNA encoding a 35-kDa antigen from Toxoplasma gondii was cloned into the CKS expression vector and expressed in Escherichia coli. By using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), the recombinant protein (rP35 antigen) was examined for reactivity with immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies in the sera of pregnant women. Of these women, 41 had a toxoplasma serologic profile suggestive of recently acquired T. gondii infection (Sabin-Feldman dye test [DT] titers from 1:256 to 1:32,000, positive IgM ELISA titers from 2.3 to 9.7, positive IgA ELISA from 1 to >28, and acute patterns in the differential agglutination [AC/HS] test) (group I), and 50 women had a toxoplasma serologic profile suggestive of infection acquired in the distant past (low DT titers from 1:16 to 1:512, negative IgM ELISA titers from 0 to 0.8, and chronic patterns in the AC/HS test) (group II). The classification of acute or chronic profile was based on the individual's clinical history as well as the combination of the results of the toxoplasma serological profile. An additional group (group III) was composed of sera from 50 women who were seronegative for T. gondii antibodies in the DT. The results revealed that whereas 85.3% of women in group I had IgG antibodies that reacted with the rP35 antigen, only 8% of women in group II had IgG antibodies that reacted with the same antigen. In immunoblots, the rP35 antigen was recognized by IgG antibodies in a pool of sera from individuals with a toxoplasma serologic profile compatible with acute infection but not in a pool of sera from individuals with a serologic profile characteristic of a chronic infection. These results reveal that IgG antibodies against the P35 antigen are produced during the acute stage of the infection but are uncommon in the latent or chronic phase of the infection. Thus, the rP35 antigen may be a useful serologic marker to differentiate between recently acquired infection and that acquired in the more distant past.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection of immunoglobulin M antibodies to P35 antigen of Toxoplasma gondii for serodiagnosis of recently acquired infection in pregnant women.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Nov;38(11):3967-70. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.11.3967-3970.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11060053 Free PMC article.
-
Serodiagnosis of recently acquired Toxoplasma gondii infection using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with a combination of recombinant antigens.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2000 Sep;7(5):781-7. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.7.5.781-787.2000. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10973455 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma gondii: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on a recombinant multi-epitope peptide for distinguishing recent from past infection in human sera.Exp Parasitol. 2013 Jan;133(1):95-100. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2012.10.016. Epub 2012 Nov 5. Exp Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23137661
-
Preparation of Toxoplasma gondii RH strain antigen, antigen analysis and antigen detection in sera: a review.Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2001;32 Suppl 2:195-201. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2001. PMID: 12041589 Review.
-
[Problems and limitations of conventional and innovative methods for the diagnosis of Toxoplasmosis in humans and animals].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):177-81. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305712 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Toxoplasma gondii recombinant antigens as tools for serodiagnosis of human toxoplasmosis: current status of studies.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2013 Sep;20(9):1343-51. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00117-13. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23784855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and Single-step Purification of GRA8 Antigen of Toxoplasma gondii in Escherichia coli.Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2011 Apr;3(2):67-77. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 23407862 Free PMC article.
-
Secretory Microneme Proteins Induce T-Cell Recall Responses in Mice Chronically Infected with Toxoplasma gondii.mSphere. 2019 Feb 27;4(1):e00711-18. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00711-18. mSphere. 2019. PMID: 30814319 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis and typing of Toxoplasma gondii.Parasit Vectors. 2015 May 28;8:292. doi: 10.1186/s13071-015-0902-6. Parasit Vectors. 2015. PMID: 26017718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TgCDPK3 regulates calcium-dependent egress of Toxoplasma gondii from host cells.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(12):e1003066. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003066. Epub 2012 Dec 4. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23226109 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ajioka J W, Boothroyd J C, Brunk B P, Hehl A, Hillier L, Manger I D, Marra M, Overton G C, Roos D S, Wan K I, Waterston R, Sibley L D. Gene discovery by EST sequencing in Toxoplasma gondii reveals sequences restricted to the ApicomplexA. Genome Res. 1998;8:18–28. - PubMed
-
- Beaman M H, McCabe R E, Wong S Y, Remington J S. Toxoplasma gondii. In: Mandel G L, Bennett J E, Dolin R, editors. Principles and practices of infectious diseases. 4th ed. New York, N.Y: Churchill Livingstone, Inc.; 1995. pp. 2455–2475.
-
- Bolling T J, Mandecki W. An Escherichia coli expression vector for high level production of heterologous proteins in fusion with CMP-KDO synthetase. BioTechniques. 1990;8:488–492. - PubMed
-
- Hedman K, Lappalainen M, Seppala I, Makela O. Recent primary toxoplasma infection indicated by a low avidity of specific IgG. J Infect Dis. 1989;159:736–740. - PubMed
-
- Johnson A M, Roberts H, Tenter A M. Evaluation of a recombinant antigen ELISA for the diagnosis of acute toxoplasmosis and comparison with traditional antigen ELISAs. J Med Microbiol. 1992;37:404–409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

