Identification of a major cluster of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from patients with liver abscess in Taiwan
- PMID: 10618128
- PMCID: PMC88736
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.1.412-414.2000
Identification of a major cluster of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from patients with liver abscess in Taiwan
Abstract
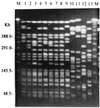
Klebsiella pneumoniae has emerged as the leading liver abscess pathogen in Taiwan, with the percentage rising from 30% in the 1980s to over 80% in the 1990s. Most of the patients with K. pneumoniae liver abscess are diabetic and without biliary tract disease. Some patients develop serious extrahepatic complications such as endophthalmitis, meningitis, lung abscess, and necrotizing fasciitis. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) was used for cluster analysis of 96 isolates from patients with liver abscess and 60 isolates from patients with other diseases. A total of 136 PFGE types were identified. Among the 96 liver abscess-associated isolates, 60 (62.5%) were classified in major cluster A. Cluster A included 41 PFGE types (types 1 to 41) which had a genetic similarity of at least 72.4% +/- 9.4%. The PFGE patterns of cluster A strains are so similar that they could have originated from the same ancestor. This study demonstrates that cluster A plays an important role in the high incidence of K. pneumoniae liver abscess in Taiwan.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess in Taiwan is not caused by a clonal spread strain.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2002 Jun;35(2):85-8. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2002. PMID: 12099340
-
Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates causing liver abscess in Taiwan.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000 Aug;37(4):279-84. doi: 10.1016/s0732-8893(00)00157-7. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000. PMID: 10974581
-
A global emerging disease of Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess: is serotype K1 an important factor for complicated endophthalmitis?Gut. 2002 Mar;50(3):420-4. doi: 10.1136/gut.50.3.420. Gut. 2002. PMID: 11839725 Free PMC article.
-
Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess: a new invasive syndrome.Lancet Infect Dis. 2012 Nov;12(11):881-7. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70205-0. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 23099082 Review.
-
Antimicrobial Resistance of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, Hypervirulence-Associated Determinants, and Resistance Mechanisms.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Nov 21;7:483. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00483. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29209595 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
FNR-Dependent RmpA and RmpA2 Regulation of Capsule Polysaccharide Biosynthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae.Front Microbiol. 2019 Oct 29;10:2436. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02436. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31736888 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology and risk factors for pyogenic liver abscess in the Calgary Health Zone revisited: a population-based study.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Sep 10;21(1):939. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06649-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34507537 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical features and development of Sepsis in Klebsiella pneumoniae infected liver abscess patients: a retrospective analysis of 135 cases.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Jun 23;21(1):597. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06325-y. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34157983 Free PMC article.
-
Liver abscess caused by magA+ Klebsiella pneumoniae in North America.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Feb;43(2):991-2. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.2.991-992.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15695726 Free PMC article.
-
IscR regulation of capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis and iron-acquisition systems in Klebsiella pneumoniae CG43.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 19;9(9):e107812. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107812. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25237815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheng D L, Liu Y-C, Yen M-Y, Liu C-Y, Wang R-S. Septic metastatic lesions of pyogenic liver abscess. Their association with Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia in diabetic patients. Arch Intern Med. 1991;151:1557–1559. - PubMed
-
- Enright M, Spratt B G. A multilocus sequence typing scheme for Streptococcus pneumoniae: identification of clones associated with serious invasive disease. Microbiology. 1998;144:3049–3060. - PubMed
-
- Frey C F, Zhu Y, Suzuki M, Isaji S. Liver abscesses. Surg Clin N Am. 1989;69:259–271. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y-C, Cheng D-L, Lin C-L. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess associated with septic endophthalmitis. Arch Intern Med. 1986;146:1913–1916. - PubMed
-
- Maiden M C J, Bygraves J A, Feil E, Morelli G, Russell J E, Urwin R, Zhang Q, Zhou J, Zurth K, Caugant D A, Feavers I M, Achtman M, Spratt B G. Multilocus sequence typing: a portable approach to the identification of clones within populations of pathogenic microorganisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:3140–3145. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

