Aspergillus Fumigatus antigen detection in sera from patients at risk for invasive aspergillosis
- PMID: 10618137
- PMCID: PMC88745
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.1.438-443.2000
Aspergillus Fumigatus antigen detection in sera from patients at risk for invasive aspergillosis
Abstract
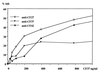
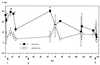
We have developed an inhibition enzyme immunoassay (inhibition-EIA) to monitor for the occurrence of invasive aspergillosis (IA) in sera from 45 immunocompromised (IC) patients. The test uses rabbit polyclonal antibodies and a mixture of components from Aspergillus fumigatus, containing three predominant antigens with molecular weights of 18,000, 33,000, and 56,000. Circulating antigens were found in five of seven proven cases of IA due to A. fumigatus. In two of the five positive cases, antigenemia was detected with inhibition-EIA earlier than with X ray or other biological methods. No antigens were detected in the sera from two patients with proven IA due to Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus terreus nor in the sera from four patients with probable IA. Circulating antigens were not detected in the control group, composed of 30 healthy adult blood donors. Four of the 32 at-risk patients examined, though they displayed no definite evidence of IA, gave a positive result in this test. The sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value of inhibition-EIA were 71.4, 94.4, and 71.2%, respectively. The data were compared with those obtained by a latex agglutination assay of galactomannan (GM) that was positive in only one patient with probable IA. The higher sensitivity obtained by inhibition-EIA may well be due to its ability to detect circulating antigens other than GM in the sera of IC patients with IA. Detecting these antigens may improve the diagnosis of IA, as they may serve as markers of this infection.
Figures
References
-
- Aisner J, Schimpff S C, Wiernik P H. Treatment of invasive aspergillosis: relation of early diagnosis and treatment to response. Ann Intern Med. 1997;86:539–544. - PubMed
-
- Ansorg R, Heintschel von Heinegg E, Rath P M. Aspergillus antigenuria compared to antigenemia in bone marrow transplant recipients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1994;13:582–589. - PubMed
-
- Bennett J E, Friedmann M M, Dupont B. Receptor-mediated clearance of Aspergillus galactomannan. J Infect Dis. 1987;155:1005–1010. - PubMed
-
- Bretagne S, Marmorat-Khoung A, Kuentz M, Latgé J-P, Bart-Delabesse E, Cordonnier C. Serum Aspergillus galactomannan antigen testing by sandwich ELISA: practical use in neutropenic patients. J Infect. 1997;35:7–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

