Inhibition of Rho-associated kinase blocks agonist-induced Ca2+ sensitization of myosin phosphorylation and force in guinea-pig ileum
- PMID: 10618150
- PMCID: PMC2269742
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.0033m.x
Inhibition of Rho-associated kinase blocks agonist-induced Ca2+ sensitization of myosin phosphorylation and force in guinea-pig ileum
Abstract
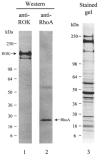
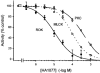
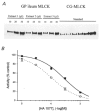
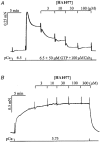
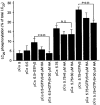
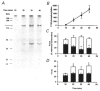
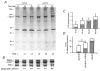
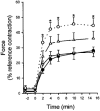
Ca2+ sensitization of smooth muscle contraction involves the small GTPase RhoA, inhibition of myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCP) and enhanced myosin regulatory light chain (LC20) phosphorylation. A potential effector of RhoA is Rho-associated kinase (ROK). The role of ROK in Ca2+ sensitization was investigated in guinea-pig ileum. Contraction of permeabilized muscle strips induced by GTPgammaS at pCa 6.5 was inhibited by the kinase inhibitors Y-27632, HA1077 and H-7 with IC50 values that correlated with the known Ki values for inhibition of ROK. GTPgammaS also increased LC20 phosphorylation and this was prevented by HA1077. Contraction and LC20 phosphorylation elicited at pCa 5.75 were, however, unaffected by HA1077. Pre-treatment of intact tissue strips with HA1077 abolished the tonic component of carbachol-induced contraction and the sustained elevation of LC20 phosphorylation, but had no effect on the transient or sustained increase in [Ca2+]i induced by carbachol. LC20 phosphorylation and contraction dynamics suggest that the ROK-mediated increase in LC20 phosphorylation is due to MLCP inhibition, not myosin light chain kinase activation. In the absence of Ca2+, GTPgammaS stimulated 35S incorporation from [35S]ATPgammaS into the myosin targeting subunit of MLCP (MYPT). The enhanced thiophosphorylation was inhibited by HA1077. No thiophosphorylation of LC20 was detected. These results indicate that ROK mediates agonist-induced increases in myosin phosphorylation and force by inhibiting MLCP activity through phosphorylation of MYPT. Under Ca2+-free conditions, ROK does not appear to phosphorylate LC20 in situ, in contrast to its ability to phosphorylate myosin in vitro. In particular, ROK activation is essential for the tonic phase of agonist-induced contraction.
Figures
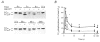

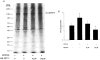
Similar articles
-
Thiophosphorylation-induced Ca(2+) sensitization of guinea-pig ileum contractility is not mediated by Rho-associated kinase.J Physiol. 2001 Jun 15;533(Pt 3):651-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.t01-2-00651.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11410624 Free PMC article.
-
ERK and p38MAPK pathways regulate myosin light chain phosphatase and contribute to Ca2+ sensitization of intestinal smooth muscle contraction.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015 Jan;27(1):135-46. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12491. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015. PMID: 25557225
-
Ca2+-independent phosphorylation of myosin in rat caudal artery and chicken gizzard myofilaments.J Physiol. 1999 May 1;516 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):805-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0805u.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10200427 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation of smooth muscle contractility by zipper-interacting protein kinase.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007 Jan;85(1):79-87. doi: 10.1139/y06-103. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17487247 Review.
-
The role of RhoA and Rho-associated kinase in vascular smooth muscle contraction.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2003 Feb;5(1):66-72. doi: 10.1007/s11906-003-0013-1. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2003. PMID: 12530938 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of Rho-kinase (ROCK-1 and ROCK-2) and its substantial role in the contractile activity of the sheep ureter.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Oct;143(3):431-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705961. Epub 2004 Sep 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15351780 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular O-GlcNAcylation augments reactivity to constrictor stimuli by prolonging phosphorylated levels of the myosin light chain.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2014 Oct;47(10):826-33. doi: 10.1590/1414-431x20144001. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2014. PMID: 25140811 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of NMDA receptor activity by F-actin and myosin light chain kinase.J Neurosci. 2001 Nov 1;21(21):8464-72. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-21-08464.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11606635 Free PMC article.
-
Agonist-induced changes in the phosphorylation of the myosin- binding subunit of myosin light chain phosphatase and CPI17, two regulatory factors of myosin light chain phosphatase, in smooth muscle.Biochem J. 2003 Jan 1;369(Pt 1):117-28. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021040. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12296769 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of PI3K promotes dilation of human small airways in a rho kinase-dependent manner.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Sep;173(18):2726-38. doi: 10.1111/bph.13542. Epub 2016 Aug 3. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27352269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akopov SE, Zhang L, Pearce WJ. Regulation of Ca2+ sensitization by PKC and rho proteins in ovine cerebral arteries: effects of artery size and age. American Journal of Physiology. 1998;275:H930–939. - PubMed
-
- Allen BG, Andrea JE, Walsh MP. Identification and characterization of protein kinase C ζ-immunoreactive proteins. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1994;269:29288–29298. - PubMed
-
- Amano M, Ito M, Kimura K, Fukata Y, Chihara K, Nakano T, Matsuura Y, Kaibuchi K. Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1996;271:20246–20249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

