Action of a NO donor on the excitation-contraction pathway activated by noradrenaline in rat superior mesenteric artery
- PMID: 10618154
- PMCID: PMC2269741
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-3-00083.x
Action of a NO donor on the excitation-contraction pathway activated by noradrenaline in rat superior mesenteric artery
Abstract
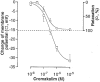
The aim of the present study was to investigate the actions of NO donors in ratsuperior mesenteric artery stimulated with noradrenaline by studying their effects on isometric tension, membrane potential (Vm), cytosolic calcium concentration ([Ca2+]cyt) and accumulation of inositol phosphates. In unstimulated arteries, SNAP (S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine, 10 microM) hyperpolarised Vm by 3.0 +/- 0.5 mV (n = 9). In KCl-stimulated arteries, SNAP relaxed contraction without changing Vm and [Ca2+]cyt. In noradrenaline-stimulated arteries, SNAP relaxed tension, repolarised Vm and decreased [Ca2+]cyt with the same potency. Responses to SNAP were unaffected by the following K+ channel blockers: glibenclamide, 4-aminopyridine, apamin and charybdotoxin, and by increasing the KCl concentration to 25 mM. In SNAP-pretreated arteries, the production of inositol phosphates and the contraction stimulated by noradrenaline were inhibited similarly. The guanylate cyclase inhibitor ODQ abolished the increase in cyclic GMP content evoked by SNAP and inhibited the effects of SNAP on contraction, Vm and accumulation of inositol phosphates in noradrenaline-stimulated artery. These results indicate that, in rat superior mesenteric arteries activated by noradrenaline, inhibition of production of inositol phosphates is responsible for the effects of the NO donor SNAP on membrane potential, [Ca2+]cyt and contraction through a cyclic GMP-dependent mechanism.
Figures

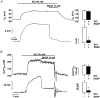
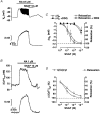

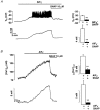
 ,
, ). The base of the columns corresponds to the level of the resting membrane potential. Data are means +
). The base of the columns corresponds to the level of the resting membrane potential. Data are means +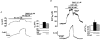
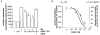
Similar articles
-
Rho-dependent kinase is involved in agonist-activated calcium entry in rat arteries.J Physiol. 2003 Sep 15;551(Pt 3):855-67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.047050. Epub 2003 Jul 9. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12853654 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of nitric oxide donors and noradrenaline on Ca2+ release sites and global intracellular Ca2+ in myocytes from guinea-pig small mesenteric arteries.J Physiol. 2002 Feb 15;539(Pt 1):25-39. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.012978. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11850499 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that different mechanisms underlie smooth muscle relaxation to nitric oxide and nitric oxide donors in the rabbit isolated carotid artery.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Apr;123(7):1351-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701746. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9579730 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of relaxation to levcromakalim by S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine (SNAP) and 8-bromo cyclic GMP in the rat isolated mesenteric artery.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Jul;124(6):1219-26. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701973. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9720794 Free PMC article.
-
The putative molecular mechanism(s) responsible for the enhanced inositol phosphate synthesis by excitatory amino acids: an overview.Neurochem Res. 1991 Jun;16(6):659-68. doi: 10.1007/BF00965552. Neurochem Res. 1991. PMID: 1686474 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Potassium Channels in Regulation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Contraction and Growth.Adv Pharmacol. 2017;78:89-144. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2016.07.001. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Adv Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28212804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rho-dependent kinase is involved in agonist-activated calcium entry in rat arteries.J Physiol. 2003 Sep 15;551(Pt 3):855-67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.047050. Epub 2003 Jul 9. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12853654 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of nitric oxide donors and noradrenaline on Ca2+ release sites and global intracellular Ca2+ in myocytes from guinea-pig small mesenteric arteries.J Physiol. 2002 Feb 15;539(Pt 1):25-39. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.012978. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11850499 Free PMC article.
-
PKD1 haploinsufficiency is associated with altered vascular reactivity and abnormal calcium signaling in the mouse aorta.Pflugers Arch. 2009 Feb;457(4):845-56. doi: 10.1007/s00424-008-0561-y. Epub 2008 Aug 5. Pflugers Arch. 2009. PMID: 18679710
-
A redox-based mechanism for the contractile and relaxing effects of NO in the guinea-pig gall bladder.J Physiol. 2001 May 1;532(Pt 3):793-810. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0793e.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11313447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Archer SL, Huang JMC, Reeve HL, Hampl V, Tolarova S, Michelakis E, Weir EK. Differential distribution of electrophysiologically distinct myocytes in conduit and resistance arteries determines their response to nitric oxide and hypoxia. Circulation Research. 1996;78:431–442. - PubMed
-
- Armstead WM. Role of activation of calcium sensitive K+ channels in NO and hypoxia induced pial artery vasodilation. American Journal of Physiology. 1997;272:H1785–1790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

