A pilot study of bacteriological population changes through potable water treatment and distribution
- PMID: 10618235
- PMCID: PMC91817
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.1.268-276.2000
A pilot study of bacteriological population changes through potable water treatment and distribution
Abstract
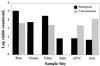
This pilot study compares the compositions of bacterial biofilms in pipe networks supplied with water containing either high levels of biodegradable organic matter (BOM) or low levels of BOM (conventionally or biologically treated, respectively). The Microbial Identification System for fatty acid analysis was utilized in this study to identify a large number of organisms (>1,400) to determine population changes in both conventionally and biologically treated water and biofilms. Data generated during this study indicated that suspended bacteria have little impact on biofilms, and despite treatment (conventional or biological), suspended microbial populations were similar following disinfection. Prechlorination with free chlorine resulted not only in reduced plate count values but also in a dramatic shift in the composition of the bacterial population to predominately gram-positive bacteria. Chlorination of biologically treated water produced the same shifts toward gram-positive bacteria. Removal of assimilable organic carbon by the biologically active filters slowed the rate of biofilm accumulation, but biofilm levels were similar to those found in conventionally treated water within several weeks. Iron pipes stimulated the rate of biofilm development, and bacterial levels on disinfected iron pipes exceeded those for chlorinated polyvinyl chloride pipes. The study showed that the iron pipe surface dramatically influenced the composition, activity, and disinfection resistance of biofilm bacteria.
Figures






References
-
- Allen M J, Geldreich E E. Proceedings of the American Water Works Association Water Quality Technology Conference. Denver, Colo: American Water Works Association; 1977. Distribution line sediments and bacterial regrowth; pp. 1–6.
-
- Arbalt R D, Slutsky A, Barber T W, Maslow J N, Niemczyk S, Falkinham III J O, O'Connor G T, Fordham von Reyn C. Genetic diversity among strains of Mycobacterium avium causing monoclonal and polyclonal bacteremia in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1993;167:1384–90. - PubMed
-
- Bablon G, Ventresque C, Aim R B. Developing a sand-GAC filter to achieve high-rate biological filtration. J Am Water Works Assoc. 1988;80(12):47–53.
-
- Bourbigot M M, Dodin A, Lheritier R. Proceedings of the American Water Works Association Annual Conference. Denver, Colo: American Water Works Association; 1982. Limiting bacterial aftergrowth in distribution systems by removing biodegradable organics; pp. 871–886.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

