Sonicated diagnostic immunoblot for bartonellosis
- PMID: 10618267
- PMCID: PMC95812
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.7.1.1-5.2000
Sonicated diagnostic immunoblot for bartonellosis
Abstract
Two simple Bartonella bacilliformis immunoblot preparation methods were developed. Antigen was prepared by two different methods: sonication of whole organisms or glycine extraction. Both methods were then tested for sensitivity and specificity. Well-defined control sera were utilized in the development of these diagnostic immunoblots, and possible cross-reactions were thoroughly examined. Sera investigated for cross-reaction with these diagnostic antigens were drawn from patients with brucellosis, chlamydiosis, Q fever, and cat scratch disease, all of whom were from regions where bartonellosis is not endemic. While both immunoblots yielded reasonable sensitivity and high specificity, we recommend the use of the sonicated immunoblot, which has a higher sensitivity when used to detect acute disease and produces fewer cross-reactions. The sonicated immunoblot reported here is 94% sensitive to chronic bartonellosis and 70% sensitive to acute bartonellosis. In a healthy group, it is 100% specific. This immunoblot preparation requires a simple sonication protocol for the harvesting of B. bacilliformis antigens and is well suited for use in regions of endemicity.
Figures
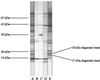
References
-
- Alexander B. A review of bartonellosis in Ecuador and Colombia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1995;52:354–359. - PubMed
-
- Amano Y, Rumbea J, Knobloch J, Olson J, Kron M. Bartonellosis in Ecuador: serosurvey and current status of cutaneous verrucous disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1997;57:174–179. - PubMed
-
- Arias-Stella J, Lieberman P H, Erlandson R A, Arias-Stella J., Jr Histology, immunohistochemistry, and ultrastructure of the verruga in Carrion's disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 1986;10:595–610. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

