Diverse karyotypic abnormalities of the c-myc locus associated with c-myc dysregulation and tumor progression in multiple myeloma
- PMID: 10618400
- PMCID: PMC26645
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.1.228
Diverse karyotypic abnormalities of the c-myc locus associated with c-myc dysregulation and tumor progression in multiple myeloma
Abstract
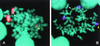
Translocations involving c-myc and an Ig locus have been reported rarely in human multiple myeloma (MM). Using specific fluorescence in situ hybridization probes, we show complex karyotypic abnormalities of the c-myc or L-myc locus in 19 of 20 MM cell lines and approximately 50% of advanced primary MM tumors. These abnormalities include unusual and complex translocations and insertions that often juxtapose myc with an IgH or IgL locus. For two advanced primary MM tumors, some tumor cells contain a karyotypic abnormality of the c-myc locus, whereas other tumor cells do not, indicating that this karyotypic abnormality of c-myc occurs as a late event. All informative MM cell lines show monoallelic expression of c-myc. For Burkitt's lymphoma and mouse plasmacytoma tumors, balanced translocation that juxtaposes c-myc with one of the Ig loci is an early, invariant event that is mediated by B cell-specific DNA modification mechanisms. By contrast, for MM, dysregulation of c-myc apparently is caused principally by complex genomic rearrangements that occur during late stages of MM progression and do not involve B cell-specific DNA modification mechanisms.
Figures


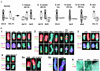
References
-
- Wiener F, Potter M. In: The Causes And Consequences Of Chromosomal Aberrations. Kirsch I R, editor. New York: CRC; 1993. pp. 91–124.
-
- Dalla-Favera R. In: The Causes And Consequences Of Chromosomal Aberrations. Kirsch I R, editor. New York: CRC; 1993. pp. 313–332.
-
- Korsmeyer S J. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:785–807. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

