Rescue of hearing, auditory hair cells, and neurons by CEP-1347/KT7515, an inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation
- PMID: 10627579
- PMCID: PMC6774096
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-01-00043.2000
Rescue of hearing, auditory hair cells, and neurons by CEP-1347/KT7515, an inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation
Abstract
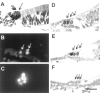
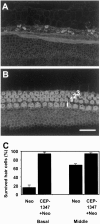
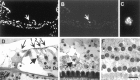
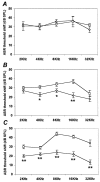
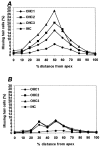
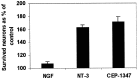
We have studied the mechanisms of auditory hair cell death after insults in vitro and in vivo. We show DNA fragmentation of hair cell nuclei after ototoxic drug and intense noise trauma. By using phospho-specific c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK) and c-Jun antibodies in immunohistochemistry, we show that the JNK pathway, associated with stress, injury, and apoptosis, is activated in hair cells after trauma. CEP-1347, a derivative of the indolocarbazole K252a, is a small molecule that has been shown to attenuate neurodegeneration by blocking the activation of JNK (). Subcutaneously delivered CEP-1347 attenuated noise-induced hearing loss. The protective effect was demonstrated by functional tests, which showed less hearing threshold shift in CEP-1347-treated than in nontreated guinea pigs, and by morphometric methods showing less hair cell death in CEP-1347-treated cochleas. In organotypic cochlear cultures, CEP-1347 prevented neomycin-induced hair cell death. In addition to hair cells, CEP-1347 promoted survival of dissociated cochlear neurons. These results suggest that therapeutic intervention in the JNK signaling cascade, possibly by using CEP-1347, may offer opportunities to treat inner ear injuries.
Figures
References
-
- Basile AS, Huang J-M, Xie C, Webster D, Berlin C, Skolnik P. N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonists limit aminoglycoside antibiotic-induced hearing loss. Nat Med. 1996;2:1338–1343. - PubMed
-
- Behrens A, Sibilia M, Wagner E. Amino-terminal phosphorylation of c-Jun regulates stress-induced apoptosis and cellular proliferation. Nat Genet. 1999;21:326–329. - PubMed
-
- Borasio GD, Horstmann S, Anneser JMH, Neff NT, Glicksman MA. CEP-1347/KT7515, a JNK pathway inhibitor, supports the in vitro survival of chick embryonic neurons. NeuroReport. 1998;9:1435–1439. - PubMed
-
- Clerici WJ, Hensley K, DiMartino DL, Butterfield DA. Direct detection of ototoxicant-induced reactive oxygen species generation in cochlear explants. Hear Res. 1996;98:116–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
