PR48, a novel regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A, interacts with Cdc6 and modulates DNA replication in human cells
- PMID: 10629059
- PMCID: PMC85219
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.3.1021-1029.2000
PR48, a novel regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A, interacts with Cdc6 and modulates DNA replication in human cells
Abstract
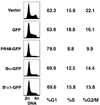
Initiation of DNA replication in eukaryotes is dependent on the activity of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), but specific phosphoprotein substrates pertinent to this requirement have not been identified. A novel regulatory subunit of PP2A, termed PR48, was identified by a yeast two-hybrid screen of a human placental cDNA library, using human Cdc6, an essential component of prereplicative complexes, as bait. PR48 binds specifically to an amino-terminal segment of Cdc6 and forms functional holoenzyme complexes with A and C subunits of PP2A. PR48 localizes to the nucleus of mammalian cells, and its forced overexpression perturbs cell cycle progression, causing a G(1) arrest. These results suggest that dephosphorylation of Cdc6 by PP2A, mediated by a specific interaction with PR48, is a regulatory event controlling initiation of DNA replication in mammalian cells.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation-independent association of CXCR2 with the protein phosphatase 2A core enzyme.J Biol Chem. 2001 May 18;276(20):16960-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M009292200. Epub 2001 Feb 26. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11278485 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a new family of protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunits.J Biol Chem. 1995 Nov 3;270(44):26123-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.44.26123. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7592815
-
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae type 2A protein phosphatase Pph22p is biochemically different from mammalian PP2A.Eur J Biochem. 2002 Jul;269(14):3372-82. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02965.x. Eur J Biochem. 2002. PMID: 12135475
-
Carboxyl methylation of the phosphoprotein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit promotes its functional association with regulatory subunits in vivo.EMBO J. 2000 Nov 1;19(21):5672-81. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.21.5672. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 11060018 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the cell cycle by protein phosphatase 2A in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006 Jun;70(2):440-9. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00049-05. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16760309 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PP2A holoenzymes, substrate specificity driving cellular functions and deregulation in cancer.Adv Cancer Res. 2019;144:55-93. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Apr 12. Adv Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31349904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) is a positive regulator of DNA replication in the Xenopus in vitro system.Cell Cycle. 2020 Jul;19(14):1817-1832. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1782589. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Cell Cycle. 2020. PMID: 32573322 Free PMC article.
-
B55alpha PP2A holoenzymes modulate the phosphorylation status of the retinoblastoma-related protein p107 and its activation.J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 24;285(39):29863-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.162354. Epub 2010 Jul 27. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20663872 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin association of human origin recognition complex, cdc6, and minichromosome maintenance proteins during the cell cycle: assembly of prereplication complexes in late mitosis.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Nov;20(22):8602-12. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.22.8602-8612.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11046155 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics in Turner syndrome.Clin Epigenetics. 2018 Apr 6;10:45. doi: 10.1186/s13148-018-0477-0. eCollection 2018. Clin Epigenetics. 2018. PMID: 29636833 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bell S P, Mitchell J, Leber J, Kobayashi R, Stillman B. The multidomain structure of ORC1p reveals similarity to regulators of DNA replication and transcriptional silencing. Cell. 1995;83:563–568. - PubMed
-
- Coleman T R, Carpenter P B, Dunphy W G. The Xenopus Cdc6 protein is essential for the initiation of a single round of DNA replication in cell-free extracts. Cell. 1996;87:53–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
