Interaction of a mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling module with the neuronal protein JIP3
- PMID: 10629060
- PMCID: PMC85220
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.3.1030-1043.2000
Interaction of a mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling module with the neuronal protein JIP3
Abstract
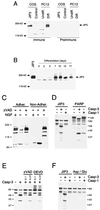
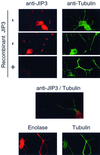
The c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) group of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) is activated in response to the treatment of cells with inflammatory cytokines and by exposure to environmental stress. JNK activation is mediated by a protein kinase cascade composed of a MAPK kinase and a MAPK kinase kinase. Here we describe the molecular cloning of a putative molecular scaffold protein, JIP3, that binds the protein kinase components of a JNK signaling module and facilitates JNK activation in cultured cells. JIP3 is expressed in the brain and at lower levels in the heart and other tissues. Immunofluorescence analysis demonstrated that JIP3 was present in the cytoplasm and accumulated in the growth cones of developing neurites. JIP3 is a member of a novel class of putative MAPK scaffold proteins that may regulate signal transduction by the JNK pathway.
Figures










References
-
- Adachi-Yamada T, Fujimura-Kamada K, Nishida Y, Matsumoto K. Distortion of proximodistal information causes JNK-dependent apoptosis in Drosophila wing. Nature. 1999;400:166–169. - PubMed
-
- Ammerer G. Sex, stress and integrity: the importance of MAP kinases in yeast. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994;4:90–95. - PubMed
-
- Bardwell L, Thorner J. A conserved motif at the amino termini of MEKs might mediate high-affinity interaction with the cognate MAPKs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996;21:373–374. - PubMed
-
- Behrens A, Sibilia M, Wagner E F. Amino-terminal phosphorylation of c-Jun regulates stress-induced apoptosis and cellular proliferation. Nat Genet. 1999;21:326–329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
