De novo facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy: frequent somatic mosaicism, sex-dependent phenotype, and the role of mitotic transchromosomal repeat interaction between chromosomes 4 and 10
- PMID: 10631134
- PMCID: PMC1288331
- DOI: 10.1086/302730
De novo facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy: frequent somatic mosaicism, sex-dependent phenotype, and the role of mitotic transchromosomal repeat interaction between chromosomes 4 and 10
Abstract
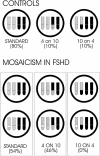
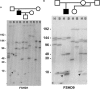
Autosomal dominant facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) is caused by deletion of most copies of the 3.3-kb subtelomeric D4Z4 repeat array on chromosome 4q. The molecular mechanisms behind the deletion and the high proportion of new mutations have remained elusive. We surveyed 35 de novo FSHD families and found somatic mosaicism in 40% of cases, in either the patient or an asymptomatic parent. Mosaic males were typically affected; mosaic females were more often the unaffected parent of a nonmosaic de novo patient. A genotypic-severity score, composed of the residual repeat size and the degree of somatic mosaicism, yields a consistent relationship with severity and age at onset of disease. Mosaic females had a higher proportion of somatic mosaicism than did mosaic males. The repeat deletion is significantly enhanced by supernumerary homologous repeat arrays. In 10% of normal chromosomes, 4-type repeat arrays are present on chromosome 10. In mosaic individuals, 4-type repeats on chromosome 10 are almost five times more frequent. The reverse configuration, also 10% in normal chromosomes, was not found, indicating that mutations may arise from transchromosomal interaction, to which the increase in 4-type repeat clusters is a predisposing factor. The somatic mosaicism suggests a mainly mitotic origin; mitotic interchromosomal gene conversion or translocation between fully homologous 4-type repeat arrays may be a major mechanism for FSHD mutations.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim (for FSHD [MIM 158900])
References
-
- Bakker E, Van Broeckhoven C, Bonten EJ, van de Vooren MJ, Veenema H, Van Hul W, Van Ommen GJ, et al (1987) Germline mosaicism and Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutations. Nature 329:554–556 - PubMed
-
- Bakker E, Wijmenga C, Vossen RH, Padberg GW, Hewitt J, van der Wielen M, Rasmussen K, et al (1995) The FSHD-linked locus D4F104S1 (p13E-11) on 4q35 has a homologue on 10qter. Muscle Nerve 2:S39–S44 - PubMed
-
- Becker J, Schwaab R, Moller-Taube A, Schwaab U, Schmidt W, Brackmann HH, Grimm T, et al (1996) Characterization of the factor VIII defect in 147 patients with sporadic hemophilia A: family studies indicate a mutation type–dependent sex ratio of mutation frequencies. Am J Hum Genet 58:657–670 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

