Duplication of 7p11.2-p13, including GRB10, in Silver-Russell syndrome
- PMID: 10631135
- PMCID: PMC1288348
- DOI: 10.1086/302717
Duplication of 7p11.2-p13, including GRB10, in Silver-Russell syndrome
Abstract
Silver-Russell syndrome (SRS) is characterized by pre- and postnatal growth failure and other dysmorphic features. The syndrome is genetically heterogeneous, but maternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 7 has been demonstrated in approximately 7% of cases. This suggests that at least one gene on chromosome 7 is imprinted and involved in the pathogenesis of SRS. We have identified a de novo duplication of 7p11.2-p13 in a proband with features characteristic of SRS. FISH confirmed the presence of a tandem duplication encompassing the genes for growth factor receptor-binding protein 10 (GRB10) and insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins 1 and 3 (IGFBP1 and -3) but not that for epidermal growth factor-receptor (EGFR). Microsatellite markers showed that the duplication was of maternal origin. These findings provide the first evidence that SRS may result from overexpression of a maternally expressed imprinted gene, rather than from absent expression of a paternally expressed gene. GRB10 lies within the duplicated region and is a strong candidate, since it is a known growth suppressor. Furthermore, the mouse homologue (Grb10/Meg1) is reported to be maternally expressed and maps to the imprinted region of proximal mouse chromosome 11 that demonstrates prenatal growth failure when it is maternally disomic. We have demonstrated that the GRB10 genomic interval replicates asynchronously in human lymphocytes, suggestive of imprinting. An additional 36 SRS probands were investigated for duplication of GRB10, but none were found. However, it remains possible that GRB10 and/or other genes within 7p11.2-p13 are responsible for some cases of SRS.
Figures

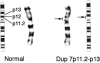
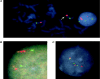

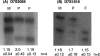
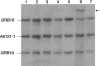
Comment in
-
Conflicting reports of imprinting status of human GRB10 in developing brain: how reliable are somatic cell hybrids for predicting allelic origin of expression?Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Feb;68(2):543-5. doi: 10.1086/318192. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11170901 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Genetic Location Database, http://cedar.genetics.soton.ac.uk/public_html/
-
- Human chromosome 7, Washington University, St Louis, http://www.genetics.wustl.edu
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim (for Silver-Russell syndrome [MIM 180860])
References
-
- Carnevale A, Frias S, del Castillo V (1978) Partial trisomy of the short arm of chromosome 7 due to familial translocation rcp(7;14)(p11;p11). Clin Genet 14:202–206 - PubMed
-
- Cattanach BM, Kirk M (1985) Differential activity of maternally and paternally derived chromosome regions in mice. Nature 315:496–498 - PubMed
-
- Chauvel PJ, Moore CM, Hasla, RHA (1975) Trisomy 18 mosaicism with features of Russell-Silver syndrome. Dev Med Child Neurol 17:220–224 - PubMed
-
- Duncan PA, Hall JG, Shapiro LR, Vibert BK (1990) Three generation dominant transmission of the Silver-Russell syndrome. Am J Med Genet 35:245–250 - PubMed
-
- Gunaratne P, Nakao M, Ledbetter D, Sutcliff J, Chinault C (1995) Tissue-specific and allele-specific replication timing control in the imprinted human Prader-Willi syndrome region. Genes Dev 9:808–820 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

