Altering expression of cinnamic acid 4-hydroxylase in transgenic plants provides evidence for a feedback loop at the entry point into the phenylpropanoid pathway
- PMID: 10631254
- PMCID: PMC58849
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.122.1.107
Altering expression of cinnamic acid 4-hydroxylase in transgenic plants provides evidence for a feedback loop at the entry point into the phenylpropanoid pathway
Abstract
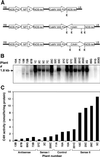
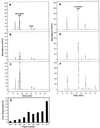
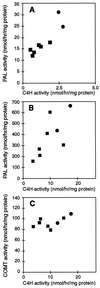
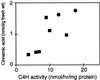
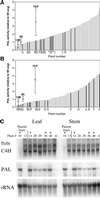
Pharmacological evidence implicates trans-cinnamic acid as a feedback modulator of the expression and enzymatic activity of the first enzyme in the phenylpropanoid pathway, L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL). To test this hypothesis independently of methods that utilize potentially non-specific inhibitors, we generated transgenic tobacco lines with altered activity levels of the second enzyme of the pathway, cinnamic acid 4-hydroxylase (C4H), by sense or antisense expression of an alfalfa C4H cDNA. PAL activity and levels of phenylpropanoid compounds were reduced in leaves and stems of plants in which C4H activity had been genetically down-regulated. However, C4H activity was not reduced in plants in which PAL activity had been down-regulated by gene silencing. In crosses between a tobacco line over-expressing PAL from a bean PAL transgene and a C4H antisense line, progeny populations harboring both the bean PAL sense and C4H antisense transgenes had significantly lower extractable PAL activity than progeny populations harboring the PAL transgene alone. Our data provide genetic evidence for a feedback loop at the entry point into the phenylpropanoid pathway that had previously been inferred from potentially artifactual pharmacological experiments.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Colocalization of L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and cinnamate 4-hydroxylase for metabolic channeling in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis.Plant Cell. 2004 Nov;16(11):3098-109. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.024406. Epub 2004 Oct 7. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 15472080 Free PMC article.
-
Antisense and sense expression of cDNA coding for CYP73A15, a class II cinnamate 4-hydroxylase, leads to a delayed and reduced production of lignin in tobacco.Phytochemistry. 2001 Aug;57(7):1159-66. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(01)00150-9. Phytochemistry. 2001. PMID: 11430988
-
Reconstitution of the entry point of plant phenylpropanoid metabolism in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae): implications for control of metabolic flux into the phenylpropanoid pathway.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jan 23;279(4):2600-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M309951200. Epub 2003 Nov 7. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14607837
-
Modulation of auxin and cytokinin responses by early steps of the phenylpropanoid pathway.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Nov 12;18(1):278. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1477-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30419822 Free PMC article.
-
Transgene-mediated and elicitor-induced perturbation of metabolic channeling at the entry point into the phenylpropanoid pathway.Plant Cell. 1999 Aug;11(8):1537-52. doi: 10.1105/tpc.11.8.1537. Plant Cell. 1999. PMID: 10449586 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A sorghum MYB transcription factor induces 3-deoxyanthocyanidins and enhances resistance against leaf blights in maize.Molecules. 2015 Jan 30;20(2):2388-404. doi: 10.3390/molecules20022388. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25647576 Free PMC article.
-
Feedback inhibition of the general phenylpropanoid and flavonol biosynthetic pathways upon a compromised flavonol-3-O-glycosylation.J Exp Bot. 2012 Apr;63(7):2465-78. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err416. Epub 2012 Jan 16. J Exp Bot. 2012. PMID: 22249996 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of rutin accumulation with 3-O-glucosyl transferase and phenylalanine ammonia-lyase activities during the ripening of tomato fruit.Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2012 Dec;67(4):371-6. doi: 10.1007/s11130-012-0321-1. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2012. PMID: 23117480
-
Monolignol pathway 4-coumaric acid:coenzyme A ligases in Populus trichocarpa: novel specificity, metabolic regulation, and simulation of coenzyme A ligation fluxes.Plant Physiol. 2013 Mar;161(3):1501-16. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.210971. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23344904 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals biosynthesis and regulation of flavonoid in common bean seeds during grain filling.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Oct 1;24(1):916. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05593-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39354389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bate NJ, Orr J, Ni W, Meroni A, Nadler-Hassar T, Doerner PW, Dixon RA, Lamb CJ, Elkind Y. Quantitative relationship between phenylalanine ammonia-lyase levels and phenylpropanoid accumulation in transgenic tobacco identifies a rate determining step in natural product synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:7608–7612. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Batz O, Logemann E, Reinold, Hahlbrock K. Extensive reprogramming of primary and secondary metabolism by fungal elicitor or infection in parsley cells. Biol Chem. 1998;379:1127–1135. - PubMed
-
- Bolwell GP, Cramer CL, Lamb CJ, Schuch W, Dixon RA. l-Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase from Phaseolus vulgaris: modulation of the levels of active enzyme by trans-cinnamic acid. Planta. 1986;169:97–107. - PubMed
-
- Bolwell GP, Mavandad M, Miller DJ, Edwards KH, Schuch W, Dixon RA. Inhibition of mRNA levels and activities by trans-cinnamic acid in elicitor-induced bean cells. Phytochemistry. 1988;27:2109–2117.
-
- Bolwell GP, Robbins MP, Dixon RA. Metabolic changes in elicitor-treated bean cells: enzymic responses in relation to rapid changes in cell wall composition. Eur J Biochem. 1985;148:571–578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

