Calmodulin activation of an endoplasmic reticulum-located calcium pump involves an interaction with the N-terminal autoinhibitory domain
- PMID: 10631259
- PMCID: PMC58854
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.122.1.157
Calmodulin activation of an endoplasmic reticulum-located calcium pump involves an interaction with the N-terminal autoinhibitory domain
Abstract
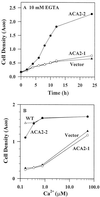
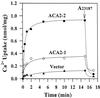
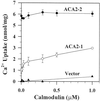
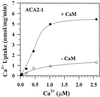
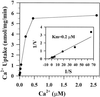
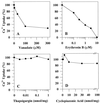
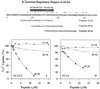
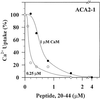
To investigate how calmodulin regulates a unique subfamily of Ca(2+) pumps found in plants, we examined the kinetic properties of isoform ACA2 identified in Arabidopsis. A recombinant ACA2 was expressed in a yeast K616 mutant deficient in two endogenous Ca(2+) pumps. Orthovanadate-sensitive (45)Ca(2+) transport into vesicles isolated from transformants demonstrated that ACA2 is a Ca(2+) pump. Ca(2+) pumping by the full-length protein (ACA2-1) was 4- to 10-fold lower than that of the N-terminal truncated ACA2-2 (Delta2-80), indicating that the N-terminal domain normally acts to inhibit the pump. An inhibitory sequence (IC(50) = 4 microM) was localized to a region within valine-20 to leucine-44, because a peptide corresponding to this sequence lowered the V(max) and increased the K(m) for Ca(2+) of the constitutively active ACA2-2 to values comparable to the full-length pump. The peptide also blocked the activity (IC(50) = 7 microM) of a Ca(2+) pump (AtECA1) belonging to a second family of Ca(2+) pumps. This inhibitory sequence appears to overlap with a calmodulin-binding site in ACA2, previously mapped between aspartate-19 and arginine-36 (J.F. Harper, B. Hong, I. Hwang, H.Q. Guo, R. Stoddard, J.F. Huang, M.G. Palmgren, H. Sze ¿1998 J Biol Chem 273: 1099-1106). These results support a model in which the pump is kept "unactivated" by an intramolecular interaction between an autoinhibitory sequence located between residues 20 and 44 and a site in the Ca(2+) pump core that is highly conserved between different Ca(2+) pump families. Results further support a model in which activation occurs as a result of Ca(2+)-induced binding of calmodulin to a site overlapping or immediately adjacent to the autoinhibitory sequence.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Autoinhibition of a calmodulin-dependent calcium pump involves a structure in the stalk that connects the transmembrane domain to the ATPase catalytic domain.J Biol Chem. 2000 Sep 29;275(39):30301-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M002047200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10818096
-
A calcium-dependent protein kinase can inhibit a calmodulin-stimulated Ca2+ pump (ACA2) located in the endoplasmic reticulum of Arabidopsis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 May 23;97(11):6224-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.11.6224. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10823962 Free PMC article.
-
A novel calmodulin-regulated Ca2+-ATPase (ACA2) from Arabidopsis with an N-terminal autoinhibitory domain.J Biol Chem. 1998 Jan 9;273(2):1099-106. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.2.1099. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9422775
-
Diversity and regulation of plant Ca2+ pumps: insights from expression in yeast.Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 2000;51:433-62. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.51.1.433. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 11543429 Review.
-
Molecular aspects of higher plant P-type Ca(2+)-ATPases.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 May 1;1465(1-2):52-78. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(00)00131-0. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 10748247 Review.
Cited by
-
Wheat Vacuolar Iron Transporter TaVIT2 Transports Fe and Mn and Is Effective for Biofortification.Plant Physiol. 2017 Aug;174(4):2434-2444. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.00672. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Plant Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28684433 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of plant p-type ATPases.Front Plant Sci. 2012 Feb 21;3:31. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00031. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22629273 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a calmodulin-regulated soybean Ca(2+)-ATPase (SCA1) that is located in the plasma membrane.Plant Cell. 2000 Aug;12(8):1393-407. doi: 10.1105/tpc.12.8.1393. Plant Cell. 2000. PMID: 10948258 Free PMC article.
-
The ACA10 Ca2+-ATPase regulates adult vegetative development and inflorescence architecture in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2008 Feb;146(2):716-28. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.108118. Epub 2007 Dec 7. Plant Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18065565 Free PMC article.
-
P-type calcium ATPases play important roles in biotic and abiotic stress signaling.Planta. 2024 Jun 26;260(2):37. doi: 10.1007/s00425-024-04462-7. Planta. 2024. PMID: 38922354 Review.
References
-
- Becker DM, Guarente L. High-efficiency transformation of yeast by electroporation. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:186–187. - PubMed
-
- Bers D, Patton C, Nuccitelli R. Methods in Cell Biology. 40: A Practical Guide to the Study of Ca2+ in Living Cells. New York: Academic Press; 1994. A practical guide to the preparation of Ca2+ buffers. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

