GABA(C) receptors control adaptive changes in a glycinergic inhibitory pathway in salamander retina
- PMID: 10632610
- PMCID: PMC6772420
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-02-00806.2000
GABA(C) receptors control adaptive changes in a glycinergic inhibitory pathway in salamander retina
Abstract
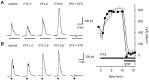
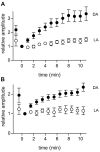
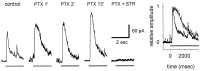
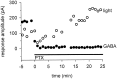
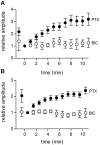
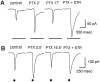
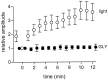
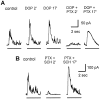
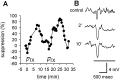
We studied the role of GABA in adaptive changes in a lateral inhibitory system in the tiger salamander retina. In dark-adapted retinal slice preparations picrotoxin caused a slow enhancement of glycine-mediated IPSCs in ganglion cells. The enhancement of glycinergic IPSCs developed slowly over the course of 5-20 min, even though picrotoxin blocked both GABA(A) and GABA(C) receptors within a few seconds. The slow enhancement of glycinergic IPSCs by picrotoxin was much weaker in light-adapted preparations. The slow enhancement of glycinergic inhibitory inputs was not produced by bicuculline, indicating that it involved GABA(C) receptors. The responses of ganglion cells to direct application of glycine were not enhanced by picrotoxin, indicating that the enhancement was not caused by an action on glycine receptors. In dark-adapted eyecup preparations picrotoxin caused a slow enhancement of glycinergic IPSPs and transient lateral inhibition produced by a rotating windmill pattern, similar to the effect of light adaptation. The results suggest that the glycinergic inhibitory inputs are modulated by an unknown substance whose synthesis and/or release is inhibited in dark-adapted retinas by GABA acting at GABA(C) receptors.
Figures
References
-
- Cook PB, McReynolds JS. Modulation of sustained and transient lateral inhibitory mechanisms in the mudpuppy retina during light adaptation. J Neurophysiol. 1998;79:197–204. - PubMed
-
- Dong CJ, Werblin FS. Temporal contrast enhancement via GABAC feedback at bipolar terminals in the tiger salamander retina. J Neurophysiol. 1998;79:2171–2180. - PubMed
-
- Dowling JE. Retinal neuromodulation: the role of dopamine. Vis Neurosci. 1991;1:87–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
