Nerve growth factor (NGF) augments cortical and hippocampal cholinergic functioning after p75NGF receptor-mediated deafferentation but impairs inhibitory avoidance and induces fear-related behaviors
- PMID: 10632613
- PMCID: PMC6772410
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-02-00834.2000
Nerve growth factor (NGF) augments cortical and hippocampal cholinergic functioning after p75NGF receptor-mediated deafferentation but impairs inhibitory avoidance and induces fear-related behaviors
Abstract
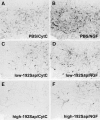
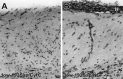
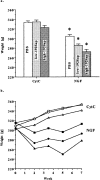
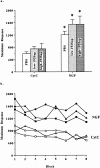
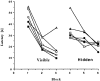
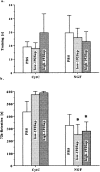
Nerve growth factor (NGF) enhances cholinergic functioning in animals with a compromised cholinergic basal forebrain (CBF). Immunotoxic lesions targeting low-affinity NGF receptor (p75NGF receptor)-bearing CBF neurons provide a selective model for testing the effects of NGF on residual cholinergic neurons. Rats received PBS or the immunotoxin 192IgG-saporin (192Sap) intracerebroventricularly at two doses (1 or 2.7 microg) known to produce different degrees of cholinergic deficit. Seven weeks after lesioning, half of each group received either NGF or cytochrome c intracerebroventricularly for 7 weeks. The two doses of 192Sap produced 50 and 80% depletions of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) activity in the neocortex and hippocampus. NGF produced the greatest increase in ChAT activity in controls, intermediate in low-lesioned, and smallest in highly lesioned animals. NGF-treated animals showed reduced weight gain, hyper-responsiveness to acoustic stimuli, and decreased inhibitory avoidance. Although general motor behavior was affected by neither 192Sap nor NGF in an open field task, highly lesioned rats took longer to reach the platform during water maze testing. Impaired spatial orientation in finding a hidden platform at the previously acquired position was mitigated by NGF. Hypertrophic changes of residual CBF neurons, Schwann cell hyperplasia, and aberrant axonal sprouting around the medulla were observed in NGF-treated animals only, independent of the preexisting lesion. Our results indicate that NGF has a limited capacity to enhance functioning of residual CBF neurons. More importantly, NGF augmented fear-related behaviors and adverse neuroproliferative changes that may restrict its therapeutic use.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes in electrocortical power and coherence in response to the selective cholinergic immunotoxin 192 IgG-saporin.Exp Brain Res. 1999 May;126(2):270-80. doi: 10.1007/s002210050736. Exp Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10369149 Free PMC article.
-
Responses of young and aged rat CNS to partial cholinergic immunolesions and NGF treatment.J Neurosci Res. 1998 May 1;52(3):322-33. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19980501)52:3<322::AID-JNR8>3.0.CO;2-F. J Neurosci Res. 1998. PMID: 9590440
-
Cholinergic control of nerve growth factor in adult rats: evidence from cortical cholinergic deafferentation and chronic drug treatment.J Neurochem. 1997 Sep;69(3):947-53. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1997.69030947.x. J Neurochem. 1997. PMID: 9282916
-
Immunolesion by 192IgG-saporin of rat basal forebrain cholinergic system: a useful tool to produce cortical cholinergic dysfunction.Prog Brain Res. 1996;109:253-64. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62109-3. Prog Brain Res. 1996. PMID: 9009714 Review.
-
The behavioral functions of the cholinergic basal forebrain: lessons from 192 IgG-saporin.Int J Dev Neurosci. 1998 Nov-Dec;16(7-8):595-602. doi: 10.1016/s0736-5748(98)00071-9. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 10198809 Review.
Cited by
-
Intrahippocampal Adeno-Associated Virus-Mediated Overexpression of Nerve Growth Factor Reverses 192IgG-Saporin-Induced Impairments of Hippocampal Plasticity and Behavior.Front Neurosci. 2021 Nov 15;15:745050. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.745050. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34867156 Free PMC article.
-
Neural stem cells and cholinergic neurons: regulation by immunolesion and treatment with mitogens, retinoic acid, and nerve growth factor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jun 10;100(12):7325-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1132092100. Epub 2003 May 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12777625 Free PMC article.
-
The cannabinergic system is implicated in the upregulation of central NGF protein by psychotropic drugs.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011 May;215(1):129-41. doi: 10.1007/s00213-010-2120-4. Epub 2010 Dec 18. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011. PMID: 21170518
-
Alleviating effects of Bushen-Yizhi formula on ibotenic acid-induced cholinergic impairments in rat.Rejuvenation Res. 2015 Apr;18(2):111-27. doi: 10.1089/rej.2014.1603. Rejuvenation Res. 2015. PMID: 25482164 Free PMC article.
-
Implication of NGF and endocannabinoid signaling in the mechanism of action of sesamol: a multi-target natural compound with therapeutic potential.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Oct;229(4):571-8. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3111-z. Epub 2013 Apr 27. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 23624775
References
-
- Aaltonen M, Riekkinen P, Sirviö J, Riekkinen P., Jr Effects of THA on passive avoidance and spatial perfrmance in quisqualic acid nucleus basalis-lesioned rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1991;39:563–567. - PubMed
-
- Bartus RT, Dean RL, III, Beer B, Lippa AS. The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science. 1982;217:408–417. - PubMed
-
- Collerton D. Cholinergic function and intellectual decline in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroscience. 1986;19:1–28. - PubMed
-
- Connor DJ, Langlais PJ, Thal LJ. Behavioral impairments after lesions of the nucleus basalis by ibotenic acid and quisqualic acid. Brain Res. 1991;555:84–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
