Treatment with anti-CD86 costimulatory molecule prevents the autoimmune lesions in murine Sjögren's syndrome (SS) through up-regulated Th2 response
- PMID: 10632675
- PMCID: PMC1905517
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01121.x
Treatment with anti-CD86 costimulatory molecule prevents the autoimmune lesions in murine Sjögren's syndrome (SS) through up-regulated Th2 response
Abstract
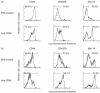
Intraperitoneal administration with anti-CD86 (B7.2) MoAb into the murine model for primary SS in NFS/sld mutant mice resulted in dramatically inhibitory effects on the development of autoimmune lesions, while no significant effects were observed when the mice were administered with anti-CD80 (B7.1) MoAb. We found that spleen cells in the murine SS model treated with anti-CD86 MoAb showed a significant impairment of autoantigen-specific T cell proliferation. T cell activation markers (CD44high, CD45RBlow, Mel-14low) were significantly down-regulated in the spleen cells gated on CD4 in anti-CD86-treated mice. We detected a higher level of cytokine production of IL-4 from splenic T cells in anti-CD86-treated mice, but not of IL-2, and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), compared with those in the anti-CD80- and PBS-treated SS model. Moreover, serum autoantibody production against alpha-fodrin autoantigen was almost entirely suppressed in anti-CD86-treated mice. These data provide strong evidence that in autoimmune exocrinopathy resembling SS in NFS/sld mutant mice, the CD86 costimulatory molecule plays a crucial role in the initiation and subsequent progression of Th1-mediated autoimmunity in the salivary and lacrimal glands.
Figures


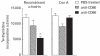
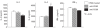
Similar articles
-
Autoantigen-specific CD4+CD28low T cell subset prevents autoimmune exocrinopathy in murine Sjögren's syndrome.J Immunol. 2000 Aug 15;165(4):2251-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.4.2251. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10925313
-
Possible role of organ-specific autoantigen for Fas ligand-mediated activation-induced cell death in murine Sjögren's syndrome.J Immunol. 2001 Nov 15;167(10):6031-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.10.6031. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11698484
-
Development of autoimmune arthritis with aging via bystander T cell activation in the mouse model of Sjögren's syndrome.Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Dec;50(12):3974-84. doi: 10.1002/art.20679. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. PMID: 15593201
-
The role of caspase cascade on the development of primary Sjögren's syndrome.J Med Invest. 2003 Feb;50(1-2):32-8. J Med Invest. 2003. PMID: 12630566 Review.
-
The role of M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor reactive T cells in Sjögren's syndrome: a critical review.J Autoimmun. 2014 Jun;51:44-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2013.12.012. Epub 2014 Jan 4. J Autoimmun. 2014. PMID: 24397962 Review.
Cited by
-
Dysregulated co-stimulatory molecule expression in a Sjögren's syndrome mouse model with potential implications by microRNA-146a.Mol Immunol. 2015 Dec;68(2 Pt C):606-16. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.09.027. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26505653 Free PMC article.
-
Regulating the regulators: costimulatory signals control the homeostasis and function of regulatory T cells.Immunol Rev. 2009 May;229(1):41-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00775.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19426214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Pathogenesis of Sjögren's Syndrome.J Immunol Res. 2021 Oct 7;2021:5928232. doi: 10.1155/2021/5928232. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 34660815 Free PMC article.
-
B7-1 and B7-2 co-stimulatory molecules are required for mercury-induced autoimmunity.Clin Exp Immunol. 2002 Jan;127(1):12-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01700.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11882027 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Mouse Models of Sjögren's Syndrome.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 30;11:1158. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01158. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32695097 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bretcher P. The two-signal model of lymphocyte activation twenty-one years later. Immunol Today. 1992;13:74–6. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz RH. Costimulation of T lymphocytes: the role of CD28, CTLA-4, and B7/BB1 in interleukin-2 production and immunotherapy. Cell. 1992;71:1065–8. - PubMed
-
- Azuma M, Ito D, Yagita H, Okumura K, Phillip JH, Lanier LL, Somoza C. B70 antigen is a second ligand for CTLA-4 and CD28. Nature. 1993;366:76–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

