Exacerbation of acute inflammatory arthritis by the colony-stimulating factors CSF-1 and granulocyte macrophage (GM)-CSF: evidence of macrophage infiltration and local proliferation
- PMID: 10632676
- PMCID: PMC1905504
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01125.x
Exacerbation of acute inflammatory arthritis by the colony-stimulating factors CSF-1 and granulocyte macrophage (GM)-CSF: evidence of macrophage infiltration and local proliferation
Abstract
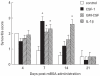
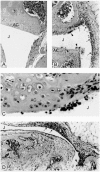
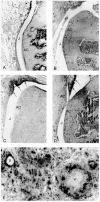
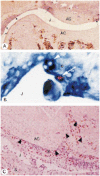
CSF-1 and GM-CSF have been implicated in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. We report the effects of CSF-1 and GM-CSF in the development of an acute methylated bovine serum albumin (mBSA)-induced murine arthritis model. Examination of histopathological features revealed that the systemic administration of CSF-1 or GM-CSF following mBSA administration into the knee resulted in the exacerbation of arthritis. This included synovial hyperplasia and joint inflammation, most evident at 7 and 14 days post-mBSA administration, and the appearance of erosive pannus tissue. The exacerbation by CSF-1 and GM-CSF was not sustained but declined in incidence and severity by 21 days post-mBSA administration, similar to the effects of IL-1beta in this model, reported here and previously. Macrophages expressing Mac-2 and F4/80 were a prominent feature of the pathology observed, particularly the infiltration of Mac-2+ macrophages seen in all mice administered CSF-1, GM-CSF or IL-1beta. Present in inflamed knees was a locally dividing population of cells which included Mac-2+ and F4/80+ macrophages. These studies demonstrate that CSF-1 and GM-CSF can exacerbate and prolong the histopathology of acute inflammatory arthritis and lend support to monocytes/macrophages being a driving influence in the pathogenesis of inflammatory arthritis.
Figures
References
-
- Metcalf D. The molecular control of cell division, differentiation commitment and maturation in haemopoieitic cells. Nature. 1989;339:27. - PubMed
-
- Firestein GS, Xu W-D, Townsend K, et al. Cytokines in chronic inflammatory arthritis. I. Failure to detect T cell lymphokines (interleukin 2 and interleukin 3) and presence of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (CSF-1) and a novel mast cell growth factor in rheumatoid synovitis. J Exp Med. 1988;168:1573–86. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hazenberg BPC, van Leeuwen MA, van Rijswijk MH, et al. Correction of granulocytopenia in Felty's syndrome by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Simultaneous induction of interleukin-6 release and flare-up of the arthritis. Blood. 1989;74:2769–70. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton JA, Butler DM, Stanton H. Cytokine interactions promoting DNA synthesis in human synovial fibroblasts. J Rheumatol. 1993;21:797–803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

