Transcription from fusion promoters generated during transposition of transposon Tn4652 is positively affected by integration host factor in Pseudomonas putida
- PMID: 10633090
- PMCID: PMC94319
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.3.589-598.2000
Transcription from fusion promoters generated during transposition of transposon Tn4652 is positively affected by integration host factor in Pseudomonas putida
Abstract
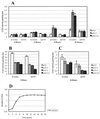
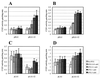
We have previously shown that both ends of the Tn3 family transposon Tn4652 contain integration host factor (IHF) binding sites and that IHF positively regulates expression of the Tn4652 transposase gene tnpA in Pseudomonas putida (R. Hõrak, and M. Kivisaar, J. Bacteriol. 180:2822-2829, 1998). Tn4652 can activate silent genes by creating fusion promoters during the transposition. The promoters are created as fusions between the -35 hexamer provided by the terminal inverted repeats of Tn4652 and the -10 hexamers in the target DNA. Two fusion promoters, PRA1 and PLA1, that contain sequences of the right and left termini of Tn4652, respectively, were chosen for the study of mechanisms of transcription activation. Gel mobility shift analysis using crude extracts from P. putida cells allowed us to detect specific binding of P. putida IHF to the ends of the transposon Tn4652. We found that the rate of transcription from the fusion promoter PRA1 is enhanced by IHF. Notably, the positive effect of IHF on transcription from the promoter PRA1 appeared only when cells of P. putida reached the stationary growth phase. We speculate that the intracellular concentration of IHF might be critical for the in vivo effect of IHF on transcription from the fusion promoters in P. putida. In the case of PLA1, the mechanism of transcription modulation by IHF is different than that observed for PRA1. Our results demonstrate that transcription of neighboring genes from outwardly directed promoters at the ends of a mobile DNA element could be influenced by the same factors that control transposition of the element.
Figures


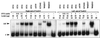
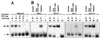

Similar articles
-
IHF is the limiting host factor in transposition of Pseudomonas putida transposon Tn4652 in stationary phase.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Mar;51(6):1773-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2003.03948.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15009901
-
Expression of the transposase gene tnpA of Tn4652 is positively affected by integration host factor.J Bacteriol. 1998 Jun;180(11):2822-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.11.2822-2829.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9603867 Free PMC article.
-
Fis negatively affects binding of Tn4652 transposase by out-competing IHF from the left end of Tn4652.Microbiology (Reading). 2009 Apr;155(Pt 4):1203-1214. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.022830-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2009. PMID: 19332822
-
Transcriptional control of the Pseudomonas putida TOL plasmid catabolic pathways.Mol Microbiol. 1993 Sep;9(5):923-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01222.x. Mol Microbiol. 1993. PMID: 7934920 Review.
-
Transcriptional control of the Pseudomonas TOL plasmid catabolic operons is achieved through an interplay of host factors and plasmid-encoded regulators.Annu Rev Microbiol. 1997;51:341-73. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.51.1.341. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9343354 Review.
Cited by
-
Colonization efficiency of Pseudomonas putida is influenced by Fis-controlled transcription of nuoA-N operon.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 2;13(8):e0201841. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201841. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30071101 Free PMC article.
-
The promoter region of lapA and its transcriptional regulation by Fis in Pseudomonas putida.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 25;12(9):e0185482. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185482. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28945818 Free PMC article.
-
Site-specific recombination system encoded by toluene catabolic transposon Tn4651.J Bacteriol. 2002 Sep;184(17):4757-66. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.17.4757-4766.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12169600 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of combination of different -10 hexamers and downstream sequences on stationary-phase-specific sigma factor sigma(S)-dependent transcription in Pseudomonas putida.J Bacteriol. 2000 Dec;182(23):6707-13. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.23.6707-6713.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 11073916 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas putida Fis binds to the lapF promoter in vitro and represses the expression of LapF.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 29;9(12):e115901. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115901. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25545773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abril M A, Buck M, Ramos J L. Activation of the Pseudomonas TOL plasmid upper pathway operon. Identification of binding sites for the positive regulator XylR and for integration host factor protein. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:15832–15838. - PubMed
-
- Bayley S A, Duggleby C J, Worsey M J, Williams P A, Hardy K G, Broda P. Two modes of loss of the TOL function from Pseudomonas putida mt-2. Mol Gen Genet. 1977;154:203–204. - PubMed
-
- Berg D E, Howe M M, editors. Mobile DNA. Washington, D.C.: American Society for Microbiology; 1989.
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

