Karyotypes of Pneumocystis carinii derived from several mammals
- PMID: 10634044
- PMCID: PMC2733205
- DOI: 10.3347/kjp.1999.37.4.271
Karyotypes of Pneumocystis carinii derived from several mammals
Abstract
Pneumocystis carinii is the most important opportunistic pathogen of humans in the world. Pneumocystis carinii is experimentally detected in the lungs of rats, mice, rabbits, and monkeys, however, the organisms from different mammals are identical in microscopic morphology. The present study tried to find out more mammalian hosts of P. carinii and also to differentiate the organisms from different mammals by karyotyping. Rats, mice, hamsters, rabbits, cats, and dogs were successfully infected by P. carinii, but guinea pigs and pigs were not. Karyotype of P. carinii from rabbits showed similar size range of chromosomes with that of the prototype, but in different pattern. The patterns from cats and dogs were also different from that of rats. The present study confirms that cats and dogs are infected by P. carinii and at least total three karyotype strains of P. carinii are proven in Korea.
Figures


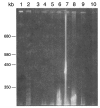
References
-
- Farrow BRH, Watson ADJ, Hartley WJ. Pneumocystis pneumonia in the dog. J Comp Pathol. 1972;82:447–453. - PubMed
-
- Hong ST, Lee M, Seo M, Choo DH, Moon HR, Lee SH. Immunoblotting analysis for serum antibodies to Pneumocystis carinii by growth and infection status of rats. Korean J Parasitol. 1995;33:187–194. - PubMed
-
- Hong ST, Park KH, Lee SH. Susceptibility of various animals to Pneumocystis carinii infection. Korean J Parasitol. 1992a;30:277–281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

