Activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway arrests cell cycle progression and differentiation of immature thymocytes in vivo
- PMID: 10637276
- PMCID: PMC2195760
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.191.2.321
Activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway arrests cell cycle progression and differentiation of immature thymocytes in vivo
Abstract
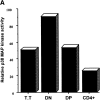
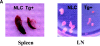
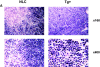
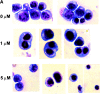
The development of T cells in the thymus is coordinated by cell-specific gene expression programs that involve multiple transcription factors and signaling pathways. Here, we show that the p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase signaling pathway is strictly regulated during the differentiation of CD4(-)CD8(-) thymocytes. Persistent activation of p38 MAP kinase blocks fetal thymocyte development at the CD25(+)CD44(-) stage in vivo, and results in the lack of T cells in the peripheral immune system of adult mice. Inactivation of p38 MAP kinase is required for further differentiation of these cells into CD4(+)CD8(+) thymocytes. The arrest of cell cycle in mitosis is partially responsible for the blockade of differentiation. Therefore, the p38 MAP kinase pathway is a critical regulatory element of differentiation and proliferation during the early stages of in vivo thymocyte development.
Figures















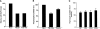



References
-
- Rodewald H.-R., Fehling H.J. Molecular and cellular events in early thymocyte development. Adv. Immmunol. 1998;69:1–113. - PubMed
-
- Glimcher L.H., Singh H. Transcription factors in lymphocyte development—T and B cells get together. Cell. 1999;96:13–23. - PubMed
-
- Clevers H., Ferrier P. Transcriptional control during T-cell development. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1998;10:166–171. - PubMed
-
- Killeen N., Irving B.A., Pippig S., Zingler K. Signaling checkpoints during the development of T lymphocytes. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1998;10:360–367. - PubMed
-
- Ip Y.T., Davis R.J. Signal transduction by the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)—from inflammation to development. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1998;10:205–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

