The immune system as a model for pattern recognition and classification
- PMID: 10641961
- PMCID: PMC61453
- DOI: 10.1136/jamia.2000.0070028
The immune system as a model for pattern recognition and classification
Abstract
Objective: To design a pattern recognition engine based on concepts derived from mammalian immune systems.
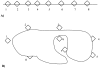
Design: A supervised learning system (Immunos-81) was created using software abstractions of T cells, B cells, antibodies, and their interactions. Artificial T cells control the creation of B-cell populations (clones), which compete for recognition of "unknowns." The B-cell clone with the "simple highest avidity" (SHA) or "relative highest avidity" (RHA) is considered to have successfully classified the unknown.
Measurement: Two standard machine learning data sets, consisting of eight nominal and six continuous variables, were used to test the recognition capabilities of Immunos-81. The first set (Cleveland), consisting of 303 cases of patients with suspected coronary artery disease, was used to perform a ten-way cross-validation. After completing the validation runs, the Cleveland data set was used as a training set prior to presentation of the second data set, consisting of 200 unknown cases.
Results: For cross-validation runs, correct recognition using SHA ranged from a high of 96 percent to a low of 63.2 percent. The average correct classification for all runs was 83.2 percent. Using the RHA metric, 11.2 percent were labeled "too close to determine" and no further attempt was made to classify them. Of the remaining cases, 85.5 percent were correctly classified. When the second data set was presented, correct classification occurred in 73.5 percent of cases when SHA was used and in 80.3 percent of cases when RHA was used.
Conclusions: The immune system offers a viable paradigm for the design of pattern recognition systems. Additional research is required to fully exploit the nuances of immune computation.
Figures




References
-
- Benjamini E, Sunshine G, Leskowitz S. Immunology: A Short Course. 3rd ed. New York: Wiley-Liss, 1996.
-
- Forrest S, Hofmeyr SA, Somayaji A. Computer immunology. Commun Assoc Comput Machinery. 1997;10:88-96.
-
- Dasgupta D, Attoh-Okine N. Immunity-based systems: a survey. Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics. 1997:369.
-
- Forrest S, Perelson AS, Allen L, Cherukuri R. Using genetic algorithms to explore pattern recognition in the immune system. Evol Comput. 1993;3:191-211.
-
- Hunt JE, Cooke DE. A learning using an artificial immune system. J Network Comput Appl. 1996;122:33-67.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

