Antiphospholipid antibodies affect trophoblast gonadotropin secretion and invasiveness by binding directly and through adhered beta2-glycoprotein I
- PMID: 10643710
- PMCID: PMC4625538
- DOI: 10.1002/1529-0131(200001)43:1<140::AID-ANR18>3.0.CO;2-P
Antiphospholipid antibodies affect trophoblast gonadotropin secretion and invasiveness by binding directly and through adhered beta2-glycoprotein I
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the in vitro ability of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) to bind human trophoblast cells and to affect gonadotropin secretion and invasiveness.
Methods: Antiphospholipid antibody IgG from women with recurrent miscarriages, beta2-glycoprotein I (beta2GPI)-independent IgG aPL human monoclonal antibody (mAb) (519), and IgM anti-beta2GPI human mAb (TMIG2) were investigated for their binding to trophoblasts cultured for various amounts of time, their ability to affect invasiveness of Matrigel-coated filters, and their release of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
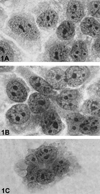
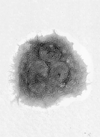
Results: Polyclonal IgG aPL, as well as mAb 519 and TMIG2, bound to trophoblasts, the highest binding being found when cells displayed the greatest amount of syncytium formation. TM1G2 binding was found to be betaGPI dependent. Both polyclonal and monoclonal aPL, but not the controls, significantly reduced hCG release and Matrigel invasiveness.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that aPL recognition of both anionic PL and adhered beta2GPI on trophoblast cell structures might represent a potential pathogenetic mechanism for defective placentation in women with the antiphospholipid syndrome.
Figures
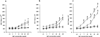
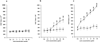
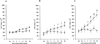

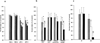
 = 3 µg/ml;
= 3 µg/ml;  = 30 µg/ml;
= 30 µg/ml;  = 60 µg/ml;
= 60 µg/ml;  = 125 µg/ml), b, human anti–β2-glycoprotein I (anti-β2GPI) monoclonal antibody (mAb) at serial protein concentrations (
= 125 µg/ml), b, human anti–β2-glycoprotein I (anti-β2GPI) monoclonal antibody (mAb) at serial protein concentrations ( = 3 µg/ml;
= 3 µg/ml;  = 12 µg/ml;
= 12 µg/ml;  = 50 µg/ml) (the effect of mAb TM1G2 was investigated in cultures performed in medium with and without fetal calf serum [FCS] or in serum-free medium with 5 µg/ml of β2GPI added), and c, human anticardiolipin mAb 519 and control mAb 57 at serial protein concentrations (
= 50 µg/ml) (the effect of mAb TM1G2 was investigated in cultures performed in medium with and without fetal calf serum [FCS] or in serum-free medium with 5 µg/ml of β2GPI added), and c, human anticardiolipin mAb 519 and control mAb 57 at serial protein concentrations ( = 3 µg/ml;
= 3 µg/ml;  = 12 µg/ml;
= 12 µg/ml;  = 50 µg/ml). Values are the mean and SD of triplicate experiments. * = P < 0.05; § = P < 0.01, APS IgG versus NHS IgG, TM1G2 versus TM1B9, and 519 versus 57.
= 50 µg/ml). Values are the mean and SD of triplicate experiments. * = P < 0.05; § = P < 0.01, APS IgG versus NHS IgG, TM1G2 versus TM1B9, and 519 versus 57.References
-
- McNeil HP, Chesterman CN, Krilis SA. Immunology and clinical importance of antiphospholipid antibodies. Adv Immunol. 1991;49:193–280. - PubMed
-
- Branch D, Dudley DJ, Mitchell MD, Creighton KA, Abbott TM, Dayanes RA. Immunoglobulin G fraction from patients with antiphospholipid antibodies caused fetal death in BALB/c mice: a model for autoimmune fetal loss. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990;63:210–216. - PubMed
-
- Piona A, La Rosa L, Tincani A, Faden D, Magro G, Grasso S, et al. Placental thrombosis and fetal loss after passive transfer of mouse lupus monoclonal or human polyclonal anti-cardiolipin antibodies in pregnant naive BALB/C mice. Scand J Immunol. 1995;41:427–432. - PubMed
-
- Roubey RA. Autoantibodies to phospholipid-binding plasma proteins: a new view of lupus anticoagulants and other phospholipid antibodies. Blood. 1994;89:2854–2867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

