ErbB2 is necessary for induction of carcinoma cell invasion by ErbB family receptor tyrosine kinases
- PMID: 10648571
- PMCID: PMC2174273
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.148.2.385
ErbB2 is necessary for induction of carcinoma cell invasion by ErbB family receptor tyrosine kinases
Abstract
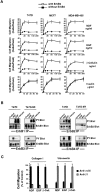
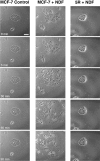
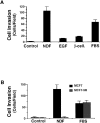
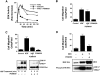
The epidermal growth factor (EGF) family of tyrosine kinase receptors (ErbB1, -2, -3, and -4) and their ligands are involved in cell differentiation, proliferation, migration, and carcinogenesis. However, it has proven difficult to link a given ErbB receptor to a specific biological process since most cells express multiple ErbB members that heterodimerize, leading to receptor cross-activation. In this study, we utilize carcinoma cells depleted of ErbB2, but not other ErbB receptor members, to specifically examine the role of ErbB2 in carcinoma cell migration and invasion. Cells stimulated with EGF-related peptides show increased invasion of the extracellular matrix, whereas cells devoid of functional ErbB2 receptors do not. ErbB2 facilitates cell invasion through extracellular regulated kinase (ERK) activation and coupling of the adaptor proteins, p130CAS and c-CrkII, which regulate the actin-myosin cytoskeleton of migratory cells. Overexpression of ErbB2 in cells devoid of other ErbB receptor members is sufficient to promote ERK activation and CAS/Crk coupling, leading to cell migration. Thus, ErbB2 serves as a critical component that couples ErbB receptor tyrosine kinases to the migration/invasion machinery of carcinoma cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extracellular-regulated kinase activation and CAS/Crk coupling regulate cell migration and suppress apoptosis during invasion of the extracellular matrix.J Cell Biol. 2000 Apr 3;149(1):223-36. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.1.223. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10747099 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin stimulates the tyrosine dephosphorylation of docking protein p130cas (Crk-associated substrate), promoting the switch of the adaptor protein crk from p130cas to newly phosphorylated insulin receptor substrate-1.Biochem J. 1998 Sep 15;334 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):595-600. doi: 10.1042/bj3340595. Biochem J. 1998. PMID: 9729467 Free PMC article.
-
Controlled activation of ErbB1/ErbB2 heterodimers promote invasion of three-dimensional organized epithelia in an ErbB1-dependent manner: implications for progression of ErbB2-overexpressing tumors.Cancer Res. 2006 May 15;66(10):5201-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4081. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16707444
-
The relative role of ErbB1-4 receptor tyrosine kinases in radiation signal transduction responses of human carcinoma cells.Oncogene. 2001 Mar 15;20(11):1388-97. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204255. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11313882 Review.
-
The ErbB/HER family of protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer.Pharmacol Res. 2014 Jan;79:34-74. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Pharmacol Res. 2014. PMID: 24269963 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of resistance to Erbitux (anti-epidermal growth factor receptor) combination therapy in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells.J Gastrointest Surg. 2004 Dec;8(8):960-9; discussion 969-70. doi: 10.1016/j.gassur.2004.09.021. J Gastrointest Surg. 2004. PMID: 15585383
-
Cas proteins: dodgy scaffolding in breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2014;16(5):443. doi: 10.1186/s13058-014-0443-5. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25606587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ErbB2 signaling network as a target for breast cancer therapy.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2006 Jan;11(1):13-25. doi: 10.1007/s10911-006-9009-1. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2006. PMID: 16947083 Review.
-
The ErbB signaling network: receptor heterodimerization in development and cancer.EMBO J. 2000 Jul 3;19(13):3159-67. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.13.3159. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 10880430 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
RNA binding protein CUGBP1 mediates the liver metastasis of colorectal cancer by regulating the ErbB signal pathway.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Jul;10(7):3373-3388. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-311. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alroy I., Yarden Y. The ErbB signaling network in embryogenesis and oncogenesissignal diversification through combinatorial ligand-receptor interactions. FEBS Lett. 1997;410:83–86 . - PubMed
-
- Bacus S.S., Gudkov A., Zelnick C.R., Chin D., Stern R., Stancovski L., Peles E., Ben-Baruch N., Farbstein H., Lupu R. Neu differentiation factor (Heregulin) induces expression of intracellular adhesion molecule 1implications for mammary tumors. Cancer Res. 1993;53:5251–5261 . - PubMed
-
- Beerli R.R., Hynes N.E. Epidermal growth factor-related peptides activate distinct subsets of ErbB receptors and differ in their biological activities. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:6071–6076 . - PubMed
-
- Beerli R.R., Wels W., Hynes N.E. Intracellular expression of single-chain antibodies reverts ErbB-2 transformation. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:23931–23936 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

