The p21(WAF1/CIP1) promoter is methylated in Rat-1 cells: stable restoration of p53-dependent p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression after transfection of a genomic clone containing the p21(WAF1/CIP1) gene
- PMID: 10648615
- PMCID: PMC85267
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.4.1291-1298.2000
The p21(WAF1/CIP1) promoter is methylated in Rat-1 cells: stable restoration of p53-dependent p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression after transfection of a genomic clone containing the p21(WAF1/CIP1) gene
Abstract
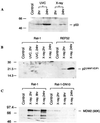
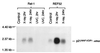
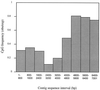
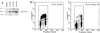
Rat-1 cells are used in many studies on transformation, cell cycle, and apoptosis. Whereas UV treatment of Rat-1 cells results in apoptosis, X-ray treatment does not induce either apoptosis or a cell cycle block. X-ray treatment of Rat-1 cells results in both an increase of p53 protein and expression of the p53-inducible gene MDM2 but not the protein or mRNA of the p53-inducible p21(WAF1/CIP1) gene, which in other cells plays an important role in p53-mediated cell cycle block. The lack of p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression appears to be the result of hypermethylation of the p21(WAF1/CIP1) promoter region, as p21(WAF1/CIP1) protein expression could be induced by growth of Rat-1 cells in the presence of 5-aza-2-deoxycytidine. Furthermore, sequence analysis of bisulfite-treated DNA demonstrated extensive methylation of cytosine residues in CpG dinucleotides in a CpG-rich island in the promoter region of the p21(WAF1/CIP1) gene. Stable X-ray-induced p53-dependent p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression and cell cycle block were restored to a Rat-1 clone after transfection with a P1 artificial chromosome (PAC) DNA clone containing a rat genomic copy of the p21(WAF1/CIP1) gene. The absence of expression of the p21(WAF1/CIP1) gene may contribute to the suitability of Rat-1 cells for transformation, cell cycle, and apoptosis studies.
Figures




References
-
- Allan L A, Fried M. p53-dependent apoptosis or growth arrest induced by different forms of radiation in U2OS cells: p21WAF1/CIP1 repression in UV induced apoptosis. Oncogene. 1999;18:5403–5412. - PubMed
-
- Balbin M, Hannon G J, Pendas A M, Ferrando A A, Vizoso F, Fueyo A, Lopez-Otin C. Functional analysis of a p21WAF1,CIP1,SDI1 mutant (Arg94→Trp) identified in a human breast carcinoma. Evidence that the mutation impairs the ability of p21 to inhibit cyclin-dependent kinases. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:15782–15786. - PubMed
-
- Bissonnette N, Hunting D J. p21-induced cycle arrest in G1 protects cells from apoptosis induced by UV-irradiation or RNA polymerase II blockage. Oncogene. 1998;16:3461–3469. - PubMed
-
- Brugarolas J, Chandrasekaran C, Gordon J I, Beach D, Jacks T, Hannon G J. Radiation-induced cell cycle arrest compromised by p21 deficiency. Nature. 1995;377:552–557. - PubMed
-
- Canman C E, Kastan M B. Small contribution of G1 checkpoint control manipulation to modulation of p53-mediated apoptosis. Oncogene. 1998;16:957–966. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
