Do centrally administered neuropeptides access cognate receptors?: an analysis in the central corticotropin-releasing factor system
- PMID: 10648719
- PMCID: PMC6774165
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-03-01142.2000
Do centrally administered neuropeptides access cognate receptors?: an analysis in the central corticotropin-releasing factor system
Abstract
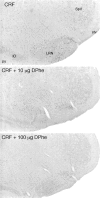
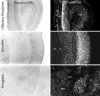
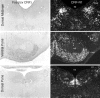
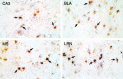
To determine the extent to which centrally administered corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) activates neurons that express CRF receptors (CRF-Rs), we followed the kinetics and distribution (relative to those of CRF-Rs) of Fos induction seen in response to intracerebroventricular (icv) injection of the peptide (1-10 microg). CRF provoked widespread Fos expression: its strength was dose-related, it peaked at 2 hr after injection, and it was antagonized in a dose-dependent manner by coinjection of CRF-R antagonists. The activation pattern closely mimicked the distribution of CRF-R1 mRNA, in including widespread Fos induction throughout the cortical mantle, in cell groups involved in sensory information processing, and in the cerebellum and several of its major afferents and targets. Dual labeling revealed extensive correspondence of CRF-stimulated Fos-immunoreactivity (Fos-ir) and CRF-R1 mRNA at these and other loci. Unique sites of CRF-R2 expression were relatively unresponsive to CRF but were more so after icv administration of urocortin (UCN), a new mammalian CRF-related peptide. Both CRF and UCN elicited activational responses in cell groups that are involved in central autonomic control but that express neither CRF-R, including the central amygdaloid and paraventricular hypothalamic nuclei, and brainstem catecholaminergic cell groups. The results support an ability of CRF-related peptides in the ventricular system to access receptor-expressing cells directly but leave open questions as to the basis for the recruitment of central autonomic structures, many of which have been identified as stress-related sites of CRF action.
Figures


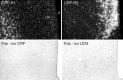
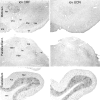
References
-
- Abercrombie M. Estimation of nuclear populations from microtome populations from microtome sections. Anat Rec. 1946;94:239–247. - PubMed
-
- Agnati LF, Zoli M, Stromberg I, Fuxe K. Intercellular communication in the brain: wiring versus volume transmission. Neuroscience. 1995;69:711–726. - PubMed
-
- Aird RB. A study of intrathecal, cerebrospinal fluid-to-brain exchange. Exp Neurol. 1984;86:342–358. - PubMed
-
- Andreae LC, Herbert J. Expression of c-fos in restricted areas of the basal forebrain and brainstem following single or combined intraventricular infusions of vasopressin and corticotropin-releasing factor. Neuroscience. 1993;53:735–748. - PubMed
-
- Arnold FJL, De Lucas Bueno M, Shiers H, Hancock DC, Evan GI, Herbert J. Expression of c-fos in regions of the basal limbic forebrain following intra-cerebroventricular corticotropin-releasing factor in unstressed or stressed male rats. Neuroscience. 1992;51:377–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
