Transient neuromotor phenotype in transgenic spastic mice expressing low levels of glycine receptor beta-subunit: an animal model of startle disease
- PMID: 10651857
- PMCID: PMC3655541
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00877.x
Transient neuromotor phenotype in transgenic spastic mice expressing low levels of glycine receptor beta-subunit: an animal model of startle disease
Abstract
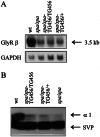
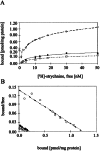
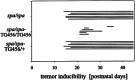
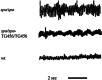
Startle disease or hereditary hyperekplexia has been shown to result from mutations in the alpha1-subunit gene of the inhibitory glycine receptor (GlyR). In hyperekplexia patients, neuromotor symptoms generally become apparent at birth, improve with age, and often disappear in adulthood. Loss-of-function mutations of GlyR alpha or beta-subunits in mice show rather severe neuromotor phenotypes. Here, we generated mutant mice with a transient neuromotor deficiency by introducing a GlyR beta transgene into the spastic mouse (spa/spa), a recessive mutant carrying a transposon insertion within the GlyR beta-subunit gene. In spa/spa TG456 mice, one of three strains generated with this construct, which expressed very low levels of GlyR beta transgene-dependent mRNA and protein, the spastic phenotype was found to depend upon the transgene copy number. Notably, mice carrying two copies of the transgene showed an age-dependent sensitivity to tremor induction, which peaked at approximately 3-4 weeks postnatally. This closely resembles the development of symptoms in human hyperekplexia patients, where motor coordination significantly improves after adolescence. The spa/spa TG456 line thus may serve as an animal model of human startle disease.
Figures
References
-
- Andermann F, Keene DL, Andermann E, Qeesney L, Qeesney F. Startle disease or hyperekplexia; further delineation of the syndrome. Brain. 1980;103:985–997. - PubMed
-
- Becker C-M, Schmieden V, Tarroni P, Strasser U, Betz H. Isoform-selective deficit of glycine receptors in the mouse mutant. Spastic. Neuron. 1992;8:283–289. - PubMed
-
- Becker C-M, Betz H, Schröder H. Expression of inhibitory glycine receptors in postnatal rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1993;26:220–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

